02配置Demo
本文最后更新于 2021-08-05 11:42:59
配置Demo
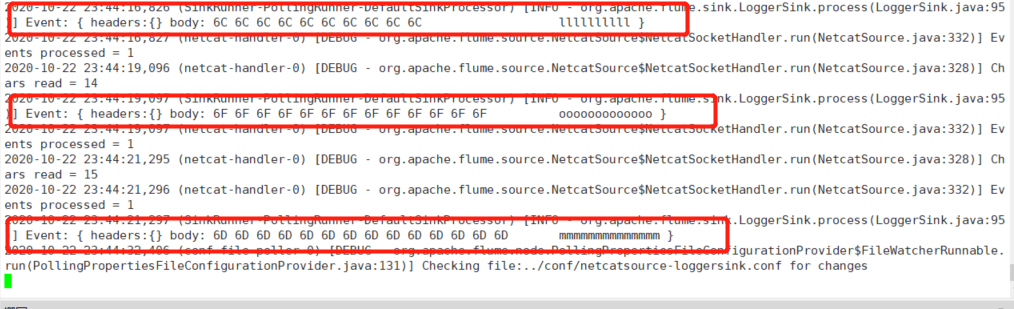
netcatsource-loggingsink
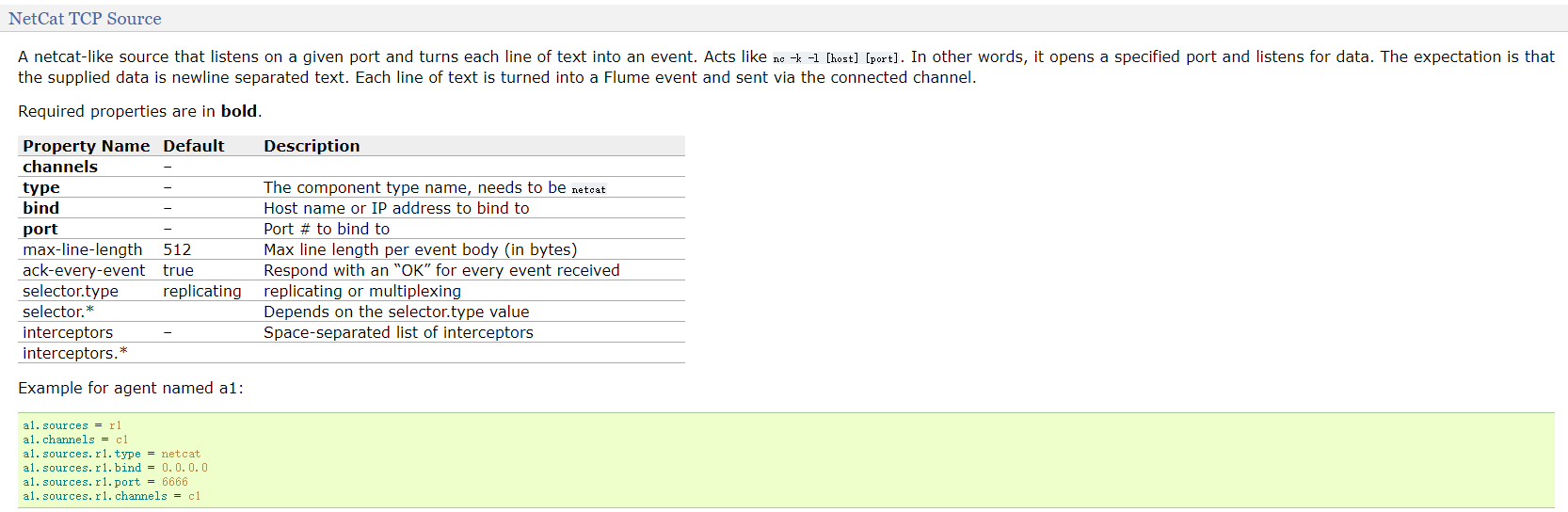
- netcat source: 作用就是监听某个tcp端口手动的数据,将每行数据封装为一个event。
工作原理类似于nc -l -k 端口
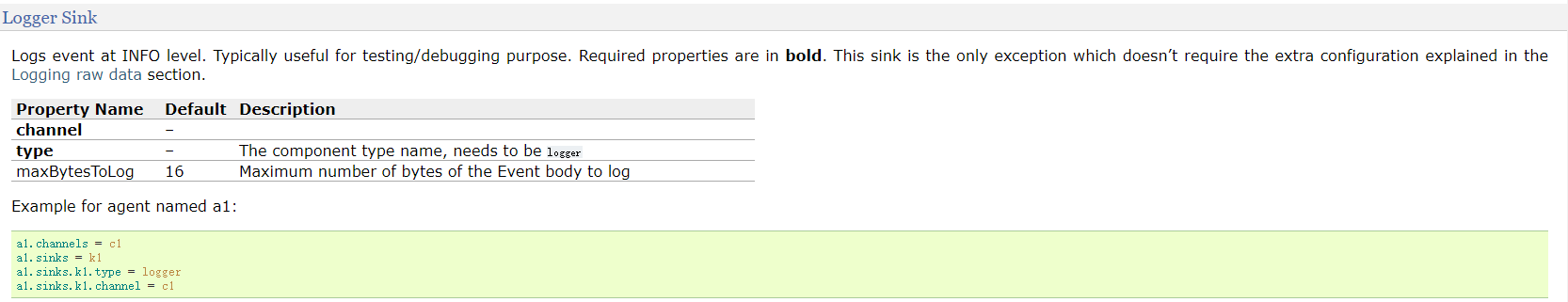
- logger sink: 作用使用logger(日志输出器)将event输出到文件或控制台,使用info级别记录event
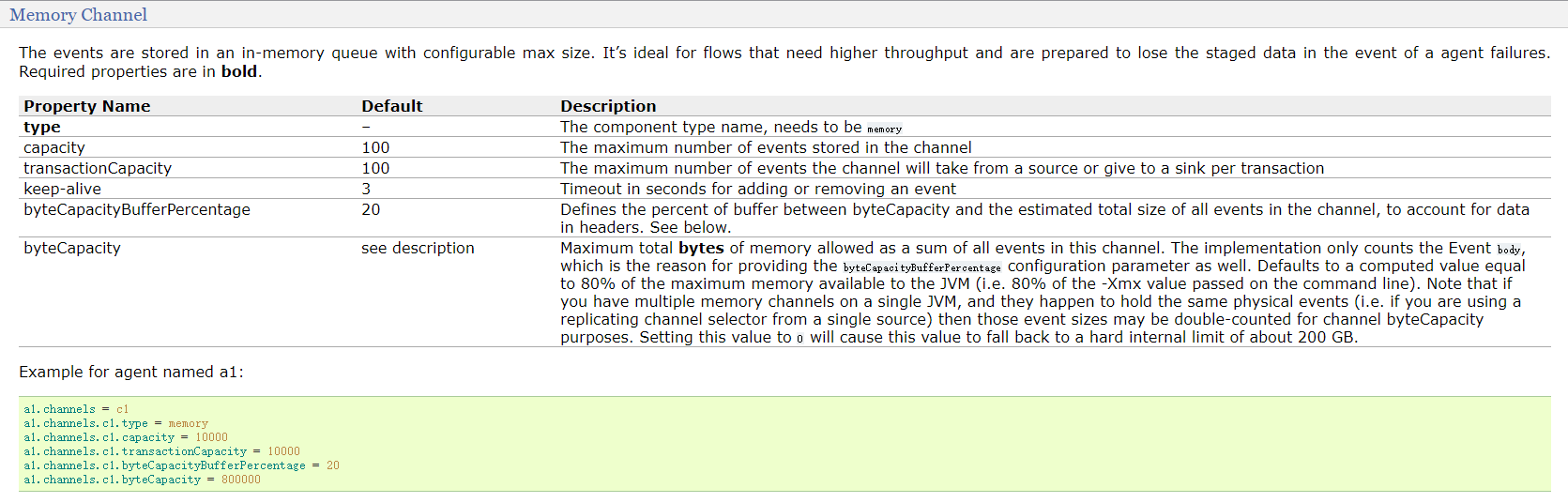
- memery channel
# sh flume-ng agent -n a1 -f ../conf/netcatsource-loggersink.conf -c ../conf
# netcatsource-loggingsink.conf
# a1是agent的名称,a1中定义了一个叫r1的source,如果有多个,使用空格间隔
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#组名名.属性名=属性值
a1.sources.r1.type=netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind=hadoop102
a1.sources.r1.port=44444
#定义sink
a1.sinks.k1.type=logger
a1.sinks.k1.maxBytesToLog=100
#定义chanel
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
#连接组件 同一个source可以对接多个channel,一个sink只能从一个channel拿数据!
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1
execsource-hdfssink
EXECSource
- execsource会在agent启动时,运行一个linux命令,运行linux命令的进程要求是一个可以持续产生数据的进程!
将标准输出的数据封装为event! - 通常情况下,如果指定的命令退出了,那么source也会退出并且不会再封装任何的数据!
- 所以使用这个source一般推荐类似cat ,tail -f 这种命令
- execsource缺点 :
- execsource和异步的source一样,无法在source向channel中放入event故障时,及时通知客户端,暂停生成数据!
容易造成数据丢失! - 比如channel满了就不能往里面放event,但是还是会一直产生数据
- execsource和异步的source一样,无法在source向channel中放入event故障时,及时通知客户端,暂停生成数据!
- execsource会在agent启动时,运行一个linux命令,运行linux命令的进程要求是一个可以持续产生数据的进程!
HDFSSink
https://flume.apache.org/releases/content/1.9.0/FlumeUserGuide.html#hdfs-sink
hdfssink将event写入到HDFS!目前只支持生成两种类型的文件: text | sequenceFile,这两种文件都可以使用压缩!
写入到HDFS的文件可以自动滚动(关闭当前正在写的文件,创建一个新文件)。基于时间、events的数量、数据大小进行周期性的滚动!
支持基于时间和采集数据的机器进行分桶和分区操作!
HDFS数据所上传的目录或文件名可以包含一个格式化的转义序列,这个路径或文件名会在上传event时,被自动替换,替换为完整的路径名!
使用此Sink要求本机已经安装了hadoop,或持有hadoop的jar包!
| Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| channel | – | |
| type | – | The component type name, needs to be hdfs |
| hdfs.path | – | HDFS directory path (eg hdfs://namenode/flume/webdata/) |
| hdfs.filePrefix | FlumeData | Name prefixed to files created by Flume in hdfs directory |
| hdfs.fileSuffix | – | Suffix to append to file (eg .avro - NOTE: period is not automatically added) |
| hdfs.inUsePrefix | – | Prefix that is used for temporal files that flume actively writes into |
| hdfs.inUseSuffix | .tmp |
Suffix that is used for temporal files that flume actively writes into |
| hdfs.emptyInUseSuffix | false | If false an hdfs.inUseSuffix is used while writing the output. After closing the output hdfs.inUseSuffix is removed from the output file name. If true the hdfs.inUseSuffix parameter is ignored an empty string is used instead. |
| hdfs.rollInterval | 30 | Number of seconds to wait before rolling current file (0 = never roll based on time interval) |
| hdfs.rollSize | 1024 | File size to trigger roll, in bytes (0: never roll based on file size) |
| hdfs.rollCount | 10 | Number of events written to file before it rolled (0 = never roll based on number of events) |
| hdfs.idleTimeout | 0 | Timeout after which inactive files get closed (0 = disable automatic closing of idle files) |
| hdfs.batchSize | 100 | number of events written to file before it is flushed to HDFS |
| hdfs.codeC | – | Compression codec. one of following : gzip, bzip2, lzo, lzop, snappy |
| hdfs.fileType | SequenceFile | File format: currently SequenceFile, DataStream or CompressedStream (1)DataStream will not compress output file and please don’t set codeC (2)CompressedStream requires set hdfs.codeC with an available codeC |
| hdfs.maxOpenFiles | 5000 | Allow only this number of open files. If this number is exceeded, the oldest file is closed. |
| hdfs.minBlockReplicas | – | Specify minimum number of replicas per HDFS block. If not specified, it comes from the default Hadoop config in the classpath. |
| hdfs.writeFormat | Writable | Format for sequence file records. One of Text or Writable. Set to Text before creating data files with Flume, otherwise those files cannot be read by either Apache Impala (incubating) or Apache Hive. |
| hdfs.threadsPoolSize | 10 | Number of threads per HDFS sink for HDFS IO ops (open, write, etc.) |
| hdfs.rollTimerPoolSize | 1 | Number of threads per HDFS sink for scheduling timed file rolling |
| hdfs.kerberosPrincipal | – | Kerberos user principal for accessing secure HDFS |
| hdfs.kerberosKeytab | – | Kerberos keytab for accessing secure HDFS |
| hdfs.proxyUser | ||
| hdfs.round | false | Should the timestamp be rounded down (if true, affects all time based escape sequences except %t) |
| hdfs.roundValue | 1 | Rounded down to the highest multiple of this (in the unit configured using hdfs.roundUnit), less than current time. |
| hdfs.roundUnit | second | The unit of the round down value - second, minute or hour. |
| hdfs.timeZone | Local Time | Name of the timezone that should be used for resolving the directory path, e.g. America/Los_Angeles. |
| hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp | false | Use the local time (instead of the timestamp from the event header) while replacing the escape sequences. |
| hdfs.closeTries | 0 | Number of times the sink must try renaming a file, after initiating a close attempt. If set to 1, this sink will not re-try a failed rename (due to, for example, NameNode or DataNode failure), and may leave the file in an open state with a .tmp extension. If set to 0, the sink will try to rename the file until the file is eventually renamed (there is no limit on the number of times it would try). The file may still remain open if the close call fails but the data will be intact and in this case, the file will be closed only after a Flume restart. |
| hdfs.retryInterval | 180 | Time in seconds between consecutive attempts to close a file. Each close call costs multiple RPC round-trips to the Namenode, so setting this too low can cause a lot of load on the name node. If set to 0 or less, the sink will not attempt to close the file if the first attempt fails, and may leave the file open or with a ”.tmp” extension. |
| serializer | TEXT |
Other possible options include avro_event or the fully-qualified class name of an implementation of the EventSerializer.Builder interface. |
| serializer.* |
#a1是agent的名称,a1中定义了一个叫r1的source,如果有多个,使用空格间隔
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#组名名.属性名=属性值
a1.sources.r1.type=exec
a1.sources.r1.command=tail -f /opt/module/hive/logs/hive.log
#定义chanel
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
#定义sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
#一旦路径中含有基于时间的转义序列,要求event的header中必须有timestamp=时间戳,如果没有需要将useLocalTimeStamp = true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://node1:9000/flume/%Y%m%d/%H/%M
#上传文件的前缀
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = logs-
# 默认是序列化文件
# 这是使用dataStream
# 还有CompressedStream压缩后的流
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
#以下三个和目录的滚动相关,目录一旦设置了时间转义序列,基于时间戳滚动
#是否将时间戳向下舍
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 10
#重新定义时间单位
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute
#是否使用本地时间戳
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 100
#以下三个和文件的滚动相关,以下三个参数是或的关系!以下三个参数如果值为0都代表禁用!
#60秒滚动生成一个新的文件
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 60
#设置每个文件到128M时滚动
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
#每写多少个event滚动一次
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
#连接组件 同一个source可以对接多个channel,一个sink只能从一个channel拿数据!
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1AvroSink-AvroSource
多个Agent串联场景
#agent1
#a1是agent的名称,a1中定义了一个叫r1的source,如果有多个,使用空格间隔
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#组名名.属性名=属性值
a1.sources.r1.type=netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind=hadoop101
a1.sources.r1.port=44444
#定义sink
a1.sinks.k1.type=avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname=hadoop102
a1.sinks.k1.port=33333
#定义chanel
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
#连接组件 同一个source可以对接多个channel,一个sink只能从一个channel拿数据!
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1
--------------------------------------------------------
#agent2
#a1是agent的名称,a1中定义了一个叫r1的source,如果有多个,使用空格间隔
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#组名名.属性名=属性值
a1.sources.r1.type=avro
a1.sources.r1.bind=hadoop102
a1.sources.r1.port=33333
#定义sink
a1.sinks.k1.type=logger
#定义chanel
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
#连接组件 同一个source可以对接多个channel,一个sink只能从一个channel拿数据!
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1ReplicatingChannelSelector
复制的channel选择器,也是默认的选择器!当一个source使用此选择器选择多个channel时,source会将event在每个channel都复制一份!
可选的channel: 向可选的channel写入event时,即便发生异常,也会忽略!
agent1: 在hadoop102
#a1是agent的名称,a1中定义了一个叫r1的source,如果有多个,使用空格间隔
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
#组名名.属性名=属性值
a1.sources.r1.type=exec
a1.sources.r1.command=tail -f /home/atguigu/test
#声明r1的channel选择器
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
#定义chanel
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
a1.channels.c2.type=memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity=1000
##定义sink
a1.sinks.k1.type=avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname=hadoop101
a1.sinks.k1.port=33333
a1.sinks.k2.type=avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname=hadoop103
a1.sinks.k2.port=33333
#连接组件 同一个source可以对接多个channel,一个sink只能从一个channel拿数据!
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1 c2
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel=c2
-------------------------------------------------------
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#组名名.属性名=属性值
a1.sources.r1.type=avro
a1.sources.r1.bind=hadoop101
a1.sources.r1.port=33333
#定义sink
a1.sinks.k1.type=logger
#定义chanel
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
#连接组件 同一个source可以对接多个channel,一个sink只能从一个channel拿数据!
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1
-------------------------------------------------------
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
#组名名.属性名=属性值
a1.sources.r1.type=avro
a1.sources.r1.bind=hadoop103
a1.sources.r1.port=33333
#定义sink
a1.sinks.k1.type=file_roll
a1.sinks.k1.sink.directory=/home/atguigu/flume
#定义chanel
a1.channels.c1.type=memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel=c1MultiPlexingChannelSelector
Multiplexing Channel Selector根据evnet header中属性,参考用户自己配置的映射信息,将event发送到指定的channel!
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1 c2 c3 c4
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing
a1.sources.r1.selector.header = state
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.CZ = c1
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.US = c2 c3
a1.sources.r1.selector.default = c4
r1中每个event根据header中key为state的值,进行选择,如果state=CZ,这类event发送到c1,
如果state=US,这类event发送到c2,c3,state=其他,发送到c4SinkProcessor
Default Sink Processor
如果agent中,只有一个sink,默认就使用Default Sink Processor,这个sink processor是不强制用户,将sink组成一个组
如果有多个sink,多个sink对接一个channel,不能选择Default Sink Processor
Failover Sink Processor
Failover Sink Processor维护了一个多个sink的有优先级的列表,按照优先级保证,至少有一个sink是可以干活的!
如果根据优先级发现,优先级高的sink故障了,故障的sink会被转移到一个故障的池中冷却!
在冷却时,故障的sink也会不管尝试发送event,一旦发送成功,此时会将故障的sink再移动到存活的池中!
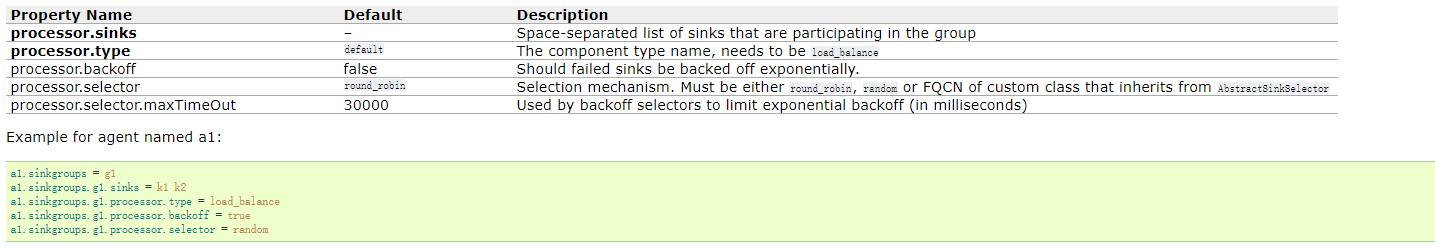
Load balancing Sink Processor
负载均衡sinkProcessor
Flume Interceptors
Timestamp Interceptor
Host Interceptor
Static Interceptor
Remove Header Interceptor
UUID Interceptor
….
Spooling Directory Source
- SpoolingDirSource指定本地磁盘的一个目录为”Spooling(自动收集)”的目录!这个source可以读取目录中新增的文件,将文件的内容封装为event!
- SpoolingDirSource在读取一整个文件到channel之后,它会采取策略,要么删除文件(是否可以删除取决于配置),要么对文件进程一个完成状态的重命名,这样可以保证source持续监控新的文件!
- SpoolingDirSource和execsource不同,SpoolingDirSource是可靠的!即使flume被杀死或重启,依然不丢数据!但是为了保证这个特性,付出的代价是,一旦flume发现以下情况,flume就会报错,停止!
- 一个文件已经被放入目录,在采集文件时,不能被修改
- 文件的名在放入目录后又被重新使用(出现了重名的文件)
- 必须已经封闭的文件才能放入到SpoolingDirSource,在同一个SpoolingDirSource中都不能出现重名的文件!

TailDirSource
- Taildir Source 可以读取多个文件最新追加写入的内容!
- Taildir Source是可靠的,即使flume出现了故障或挂掉。Taildir Source在工作时,会将读取文件的最后的位置记录在一个json文件中,一旦agent重启,会从之前已经记录的位置,继续执行tail操作!
- Json文件中,位置是可以修改,修改后,Taildir Source会从修改的位置进行tail操作!如果JSON文件丢失了,此时会重新从每个文件的第一行,重新读取,这会造成数据的重复!
- Taildir Source目前只能读文本文件!
- TailDirSource采集的文件,不能随意重命名!如果日志在正在写入时,名称为 xxxx.tmp,写入完成后,滚动,
改名为xxx.log,此时一旦匹配规则可以匹配上述名称,就会发生数据的重复采集!

a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.type = TAILDIR
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /var/log/flume/taildir_position.json
a1.sources.r1.filegroups = f1 f2
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f1 = /var/log/test1/example.log
a1.sources.r1.headers.f1.headerKey1 = value1
a1.sources.r1.filegroups.f2 = /var/log/test2/.*log.*
a1.sources.r1.headers.f2.headerKey1 = value2
a1.sources.r1.headers.f2.headerKey2 = value2-2
a1.sources.r1.fileHeader = true
a1.sources.ri.maxBatchCount = 1000HTTP Source
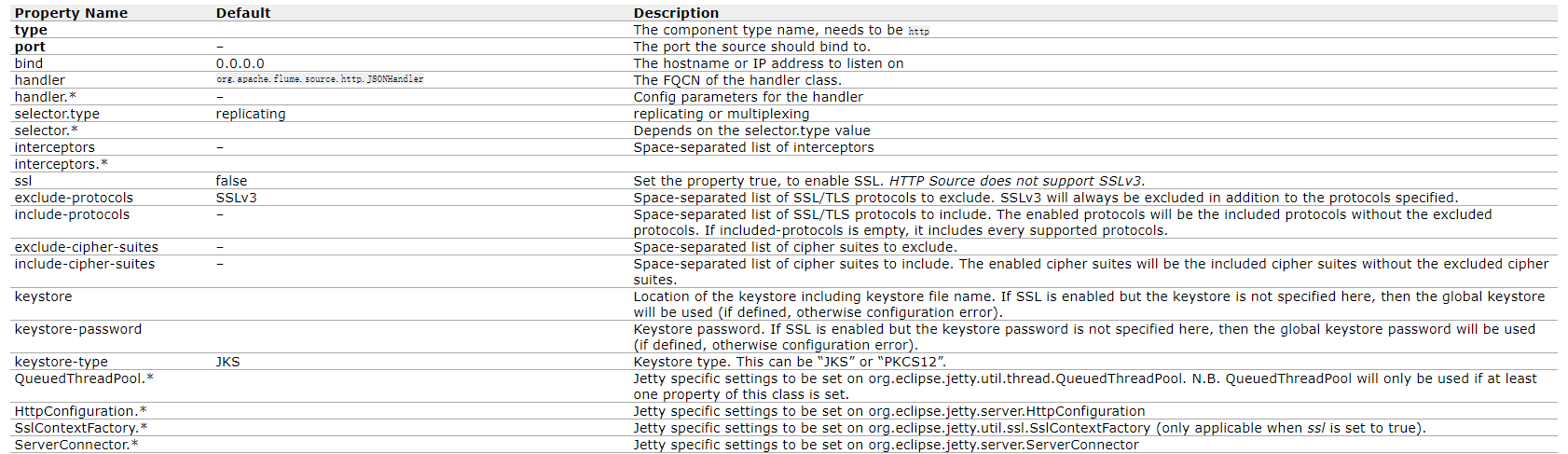
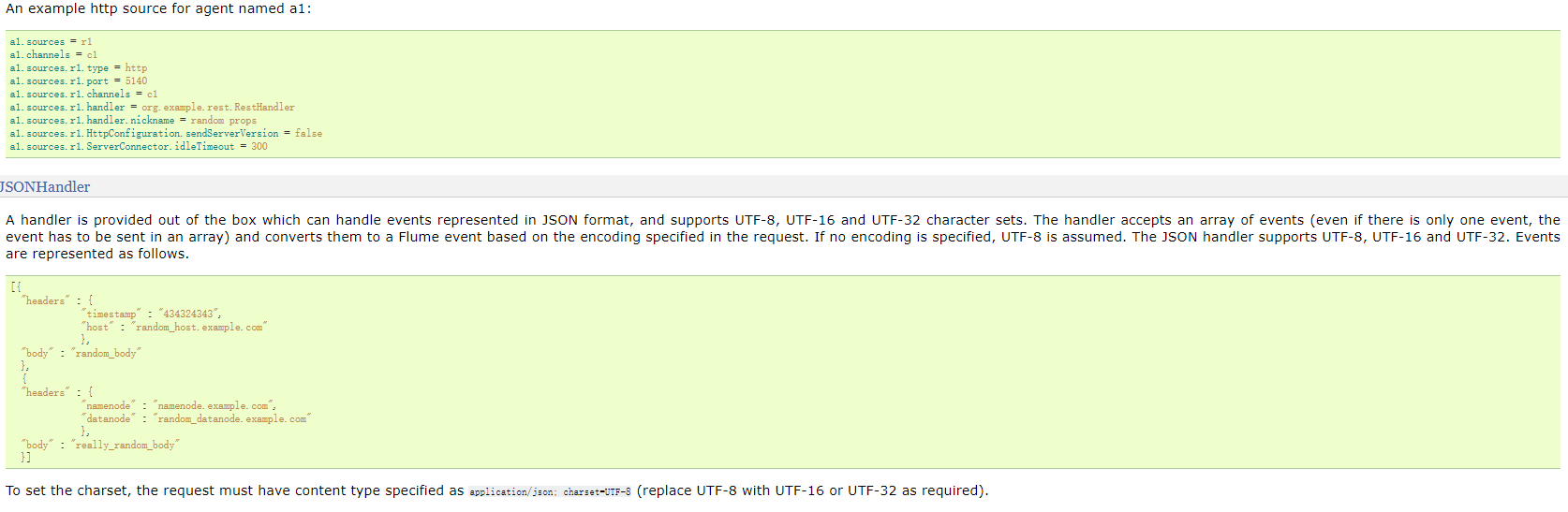
- 通过HTTP POST和GET接受Flume事件的源。GET只能用于实验。HTTP请求被一个必须实现HTTPSourceHandler接口的可插入“处理程序”转换为flume事件。这个处理程序接受一个HttpServletRequest并返回一个flume事件列表。从一个Http请求处理的所有事件都在一个事务中提交给通道。
- 在一个post请求中发送的所有事件被视为一个批处理,并插入到一个事务中的通道中。
- 这个源基于Jetty 9.4
Avro Source
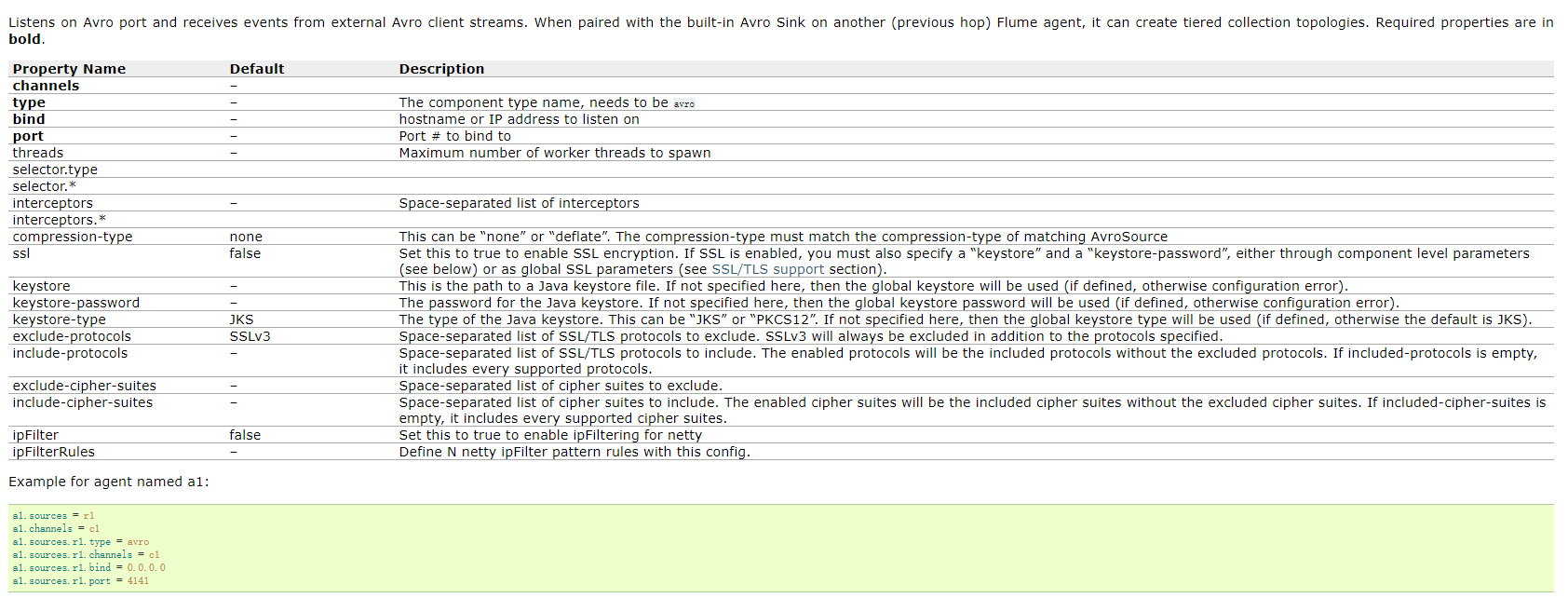
Kafka Source

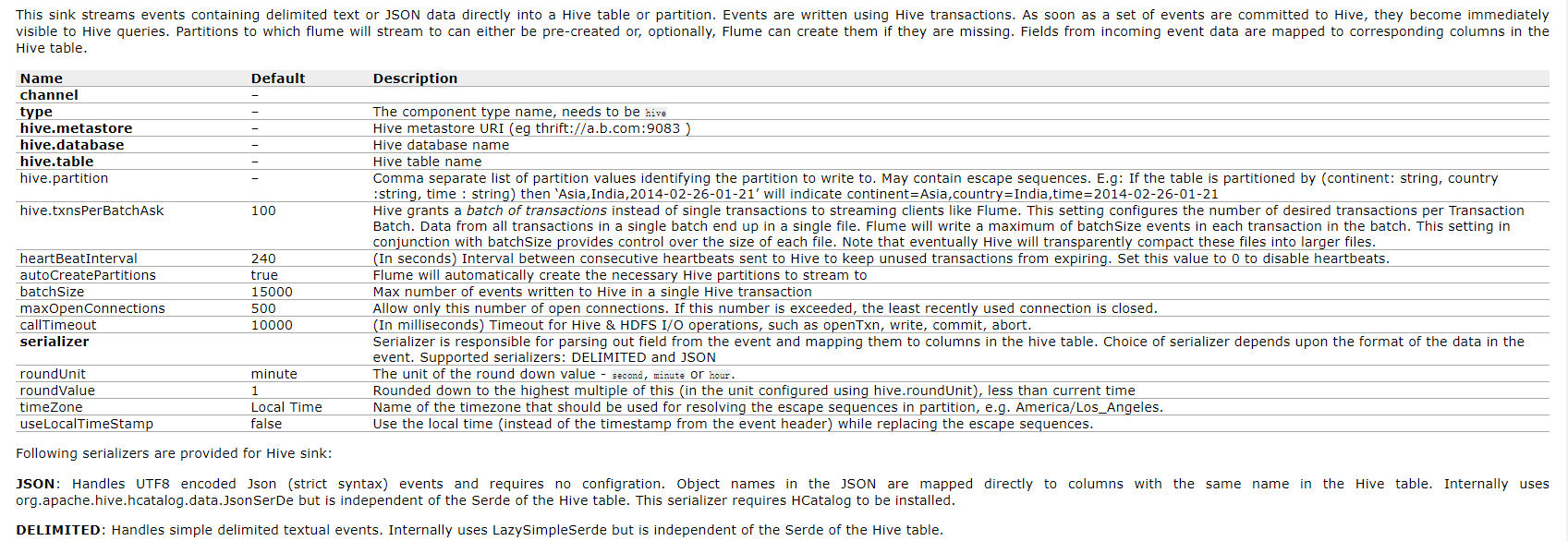
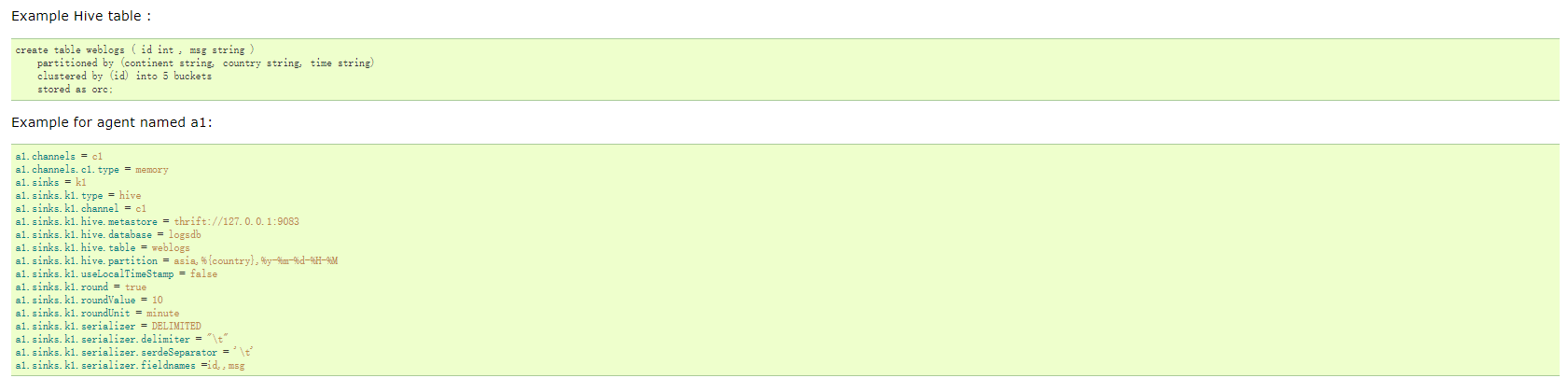
Hive Sink
Avro Sink

Kafka Sink

ElasticSearchSink