04Hystrix
Hystrix
在分布式系统中,难免有对外部接口的依赖,而外部接口有可能出现响应缓慢,大量请求超时,大量访问出现异常等情况。出现上面所说的情况有可能是由很多原因导制的,可能是网络抖动,外部系统有没有测出的bug等。因为一个接口的异常,有可能导制线程阻塞,影响到其它接口的服务,甚至整个系统的服务给拖跨,对外部系统依赖的模块越多,出现的风险也就会越高,Hystrix正是用于解决这样的问题。
简单使用
整和spring
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
//===================================================
@EnableHystrix
//====================================================
@GetMapping("/hello")
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod="helloFallBack")
public Object sayHello(String name) {
//return restTemplate.getForObject("http://producer/hello?name={n}", Object.class,name);
//等价于
HashMap<String, String> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("name",name);
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://producer/hello?name={name}", Object.class,params);
}整和fegin
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true
//=================================
@FeignClient(value = "producer" ,fallback = HelloClientFallBack.class)
//或者fallbackFactory原生
public class HelloCommand extends HystrixCommand<String> {
protected HelloCommand() {
super(Setter.withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey("test"))
.andCommandPropertiesDefaults(HystrixCommandProperties.Setter()
//开启熔断模式
.withCircuitBreakerEnabled(true)
//出现错误的比率超过30%就开启熔断
.withCircuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage(30)
//至少有10个请求才进行errorThresholdPercentage错误百分比计算
.withCircuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold(10)
//半开试探休眠时间,这里设置为3秒
.withCircuitBreakerSleepWindowInMilliseconds(3000)
)
);
}
@Override
protected String run() throws Exception {
//模拟外部请求需要的时间长度
System.out.println("执行了run方法");
Thread.sleep(2000);
return "sucess";
}
@Override
protected String getFallback() {
//当外部请求超时后,会执行fallback里的业务逻辑
System.out.println("执行了回退方法");
return "error";
}
}
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
HelloCommand command = new HelloCommand();
String result = command.execute();
System.out.println("circuit Breaker is open : " + command.isCircuitBreakerOpen());
if(command.isCircuitBreakerOpen()){
Thread.currentThread().sleep(500);
}
}
}
}
@HystrixCommand参数配置
@HystrixCommand(commandKey = "getCompanyInfoById",
groupKey = "company-info",
threadPoolKey = "company-info",
fallbackMethod = "fallbackMethod",
threadPoolProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name = "coreSize", value = "30"),
@HystrixProperty(name = "maxQueueSize", value = "101"),
@HystrixProperty(name = "keepAliveTimeMinutes", value = "2"),
@HystrixProperty(name = "queueSizeRejectionThreshold", value = "15"),
})- commandKey: 代表一个接口, 如果不配置,默认是@HystrixCommand注解修饰的函数的函数名。
- groupKey: 代表一个服务,一个服务可能会暴露多个接口。 Hystrix会根据组来组织和统计命令的告、仪表盘等信息。Hystrix命令默认的线程划分也是根据命令组来实现。默认情况下,Hystrix会让相同组名的命令使用同一个线程池,所以我们需要在创建Hystrix命令时为其指定命令组来实现默认的线程池划分。
- threadPoolKey: 对线程池进行更细粒度的配置,默认等于groupKey的值。如果依赖服务中的某个接口耗时较长,需要单独特殊处理,最好单独用一个线程池,这时候就可以配置threadpool key。也可以多个服务接口设置同一个threadPoolKey构成线程组。
- fallbackMethod:@HystrixCommand注解修饰的函数的回调函数,@HystrixCommand修饰的函数必须和这个回调函数定义在同一个类中,因为定义在了同一个类中,所以fackback method可以是public/private均可。
- 线程池配置:coreSize表示核心线程数,hystrix默认是10;maxQueueSize表示线程池的最大队列大小; keepAliveTimeMinutes表示非核心线程空闲时最大存活时间;queueSizeRejectionThreshold:该参数用来为队列设置拒绝阈值。通过该参数,即使队列没有达到最大值也能拒绝请求。
降级
服务提前配置备用措施,当故障发生时无缝启用备用方案(或者返回一些默认值),用户无感知,最终目的都是为了提供7*24小时稳定服务,这样对用户来说才是高价值、可信赖的优质服务。
线程run()抛出异常,超时,线程池或信号量满了,或短路了,都会触发fallback机制。
| 名字 | 描述 | 触发fallback |
|---|---|---|
| EMIT | 值传递 | NO |
| SUCCESS | 执行完成,没有错误 | NO |
| FAILURE | 执行抛出异常 | YES |
| TIMEOUT | 执行开始,但没有在允许的时间内完成 | YES |
| BAD_REQUEST | 执行抛出HystrixBadRequestException | NO |
| SHORT_CIRCUITED | 断路器打开,不尝试执行 | YES |
| THREAD_POOL_REJECTED | 线程池拒绝,不尝试执行 | YES |
| SEMAPHORE_REJECTED | 信号量拒绝,不尝试执行 | YES |
熔断
当请求调用失败率达到阀值自动触发降级(如因网络故障/超时造成的失败率高),熔断器触发的快速失败会进行快速恢复。
- 如果经过断路器的流量超过了一定的阈值,HystrixCommandProperties.circuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold()配置,默认20。比如,要求在10s内,经过短路器的流量必须达到20个才会去判断要不要短路;
- 如果断路器统计到的异常调用的占比超过了一定的阈值,HystrixCommandProperties.circuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage()配置。如果达到了上面的要求,比如说在10s内,经过短路器的请求达到了30个;同时其中异常的访问数量,占到了一定的比例(**默认50%**),比如60%的请求都是异常(报错,timeout,reject),会开启短路;
- 然后断路器从close状态转换到open状态;
- 断路器打开的时候,所有经过该断路器的请求全部被短路,不调用后端服务,直接走fallback降级逻辑;
- 经过了一段时间之后,HystrixCommandProperties.circuitBreakerSleepWindowInMilliseconds()配置,断路器会half-open状态,让一条请求经过短路器,看能不能正常调用。如果调用成功了,那么断路器就自动恢复,转到close状态。
隔离策略/限流
hystrix提供了两种隔离策略:线程池隔离和信号量隔离。hystrix默认采用线程池隔离。
线程池隔离:不同服务通过使用不同线程池,彼此间将不受影响,达到隔离效果。我们通过andThreadPoolKey配置使用命名为ThreadPoolTest的线程池,实现与其他命名的线程池天然隔离,如果不配置andThreadPoolKey则使用withGroupKey配置来命名线程池
信号量隔离:线程隔离会带来线程开销,有些场景(比如无网络请求场景)可能会因为用开销换隔离得不偿失,为此hystrix提供了信号量隔离,当服务的并发数大于信号量阈值时将进入fallback。通过withExecutionIsolationStrategy(ExecutionIsolationStrategy.SEMAPHORE)配置为信号量隔离,通过withExecutionIsolationSemaphoreMaxConcurrentRequests配置执行并发数不能大于3,由于信号量隔离下无论调用哪种命令执行方法,hystrix都不会创建新线程执行run()/construct(),所以调用程序需要自己创建多个线程来模拟并发调用execute(),最后看到一旦并发线程>3,后续请求都进入fallback
请求缓存
在一次请求中,如果有多个command,参数都是一样的,调用的接口也是一样的,其实结果可以认为也是一样的。这个时候,可以让第一次command执行返回的结果,被缓存在内存中,然后在这个请求上下文中,后续的其他对这个依赖的调用全部从内存中取用缓存结果就可以了。
//使用@CacheResult实现缓存功能
@CacheResult(cacheKeyMethod = "getCacheKey")
@HystrixCommand(commandKey = "findUserById", groupKey = "UserService", threadPoolKey = "userServiceThreadPool")
public UserVO findById(Long id) {
ResponseEntity<UserVO> user = restTemplate.getForEntity("http://users-service/user?id={id}", UserVO.class, id);
return user.getBody();
}
public String getCacheKey(Long id) {
return String.valueOf(id);
}
//使用@CacheResult和@CacheKey实现缓存功能
@CacheResult
@HystrixCommand(commandKey = "findUserById", groupKey = "UserService", threadPoolKey = "userServiceThreadPool")
public UserVO findById2(@CacheKey("id") Long id) {
ResponseEntity<UserVO> user = restTemplate.getForEntity("http://users-service/user?id={id}", UserVO.class, id);
return user.getBody();
}
//使用@CacheRemove清空缓存
@CacheRemove(commandKey = "findUserById")
@HystrixCommand(commandKey = "updateUser",groupKey = "UserService",threadPoolKey = "userServiceThreadPool")
public void updateUser(@CacheKey("id")UserVO user){
restTemplate.postForObject("http://users-service/user",user,UserVO.class);
}请求合并
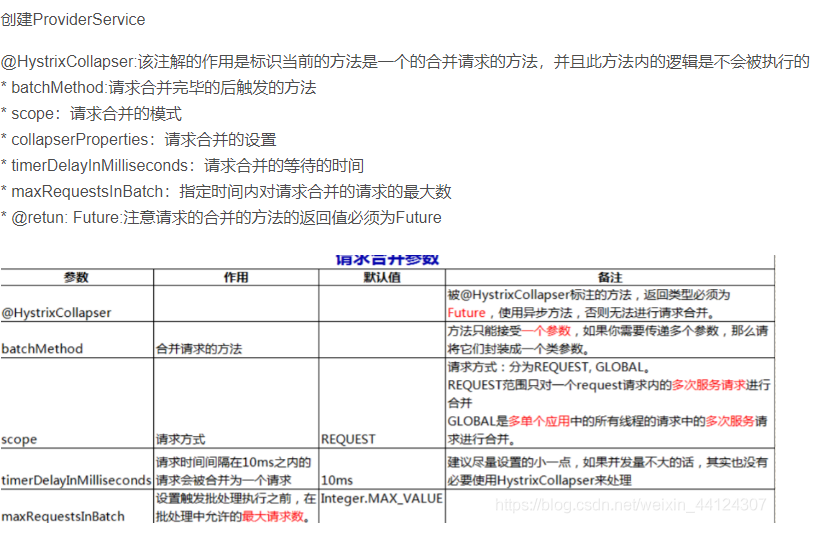
hystrix支持N个请求自动合并为一个请求,这个功能在有网络交互的场景下尤其有用,比如每个请求都要网络访问远程资源,如果把请求合并为一个,将使多次网络交互变成一次,极大节省开销。重要一点,两个请求能自动合并的前提是两者足够“近”,即两者启动执行的间隔时长要足够小,默认为10ms,即超过10ms将不自动合并。
@Service
public class ProductService
{
/**
* @param null
* @description: 1.@HystrixCollapser:该注解的作用是标识当前的方法是一个的合并请求的方法,并且此方法内的逻辑是不会被执行的
* batchMethod:请求合并完毕的后触发的方法
* scope:请求合并的模式
* collapserProperties:请求合并的设置
* timerDelayInMilliseconds:请求合并的等待的时间
* maxRequestsInBatch:指定时间内对请求合并的请求的最大数
* @retun: Future:注意请求的合并的方法的返回值必须为Future
* @author: shinelon
* @time: 2019/9/3:17:30
*/
@HystrixCollapser(batchMethod = "batchMethod", scope = com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCollapser.Scope.GLOBAL,
//请求时间间隔在 20ms 之内的请求会被合并为一个请求,默认为 10ms
collapserProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name = "timerDelayInMilliseconds", value = "20"),
//设置触发批处理执行之前,在批处理中允许的最大请求数。
@HystrixProperty(name = "maxRequestsInBatch", value = "200")
})
public Future<Product> mergeRequest(Integer id)
{
System.out.println("========+" + id + "+======");
return null;
}
/**
* 1.@HystrixCommand:表示当前的方法开启熔断
2.请求合并完毕后触发的方法,要和batchMethod 内的名字一致
3.在请求合并完毕后会将合并的参数的使用list集合的方式进行传递
*
* @return
*/
@HystrixCommand
public List<Product> batchMethod(List<Integer> ids)
{
for (Integer id : ids)
{
System.out.println(ids + "batchMethod------------");
}
//相当于调用了Provider返回的数据
List<Product> list = Arrays.asList(new Product("电视", 1), new Product("电视", 2), new Product("电视", 3), new Product("电视", 4));
return list;
}
}
监控

大概原理
@HystrixCommand解析过程

public abstract class SpringFactoryImportSelector<T>
implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware {
private final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(SpringFactoryImportSelector.class);
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
private Class<T> annotationClass;
private Environment environment;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected SpringFactoryImportSelector() {
this.annotationClass = (Class<T>) GenericTypeResolver
.resolveTypeArgument(this.getClass(), SpringFactoryImportSelector.class);
}
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
if (!isEnabled()) {
return new String[0];
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(
metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(this.annotationClass.getName(), true));
Assert.notNull(attributes, "No " + getSimpleName() + " attributes found. Is "
+ metadata.getClassName() + " annotated with @" + getSimpleName() + "?");
// Find all possible auto configuration classes, filtering duplicates
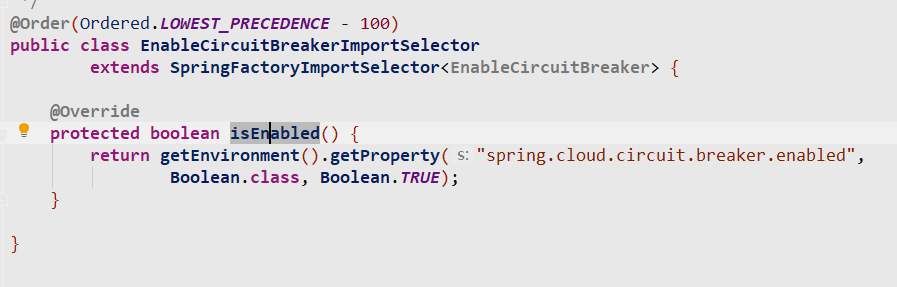
//获取到spring.factories文件中org.springframework.cloud.client.circuitbreaker.EnableCircuitBreaker
//对应的value
List<String> factories = new ArrayList<>(new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader
.loadFactoryNames(this.annotationClass, this.beanClassLoader)));
if (factories.isEmpty() && !hasDefaultFactory()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Annotation @" + getSimpleName()
+ " found, but there are no implementations. Did you forget to include a starter?");
}
if (factories.size() > 1) {
// there should only ever be one DiscoveryClient, but there might be more than
// one factory
this.log.warn("More than one implementation " + "of @" + getSimpleName()
+ " (now relying on @Conditionals to pick one): " + factories);
}
//最后把所有的EnableCircuitBreaker对应的value都注入到容器
return factories.toArray(new String[factories.size()]);
}
protected boolean hasDefaultFactory() {
return false;
}
protected abstract boolean isEnabled();
protected String getSimpleName() {
return this.annotationClass.getSimpleName();
}
protected Class<T> getAnnotationClass() {
return this.annotationClass;
}
protected Environment getEnvironment() {
return this.environment;
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = classLoader;
}
}注入了HystrixCircuitBreakerConfiguration

在configuration中又注入了一个AOP
Command
线程隔离
/**
这个方法是AbstractCommand的构造方法,里面用于初使化AbstractCommand,包括circuitBreaker 与线程池对象都在这里进行构造
**/
protected AbstractCommand(HystrixCommandGroupKey group, HystrixCommandKey key, HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixCircuitBreaker circuitBreaker, HystrixThreadPool threadPool,
HystrixCommandProperties.Setter commandPropertiesDefaults, HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter threadPoolPropertiesDefaults,
HystrixCommandMetrics metrics, TryableSemaphore fallbackSemaphore, TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore,
HystrixPropertiesStrategy propertiesStrategy, HystrixCommandExecutionHook executionHook) {
//commandGroup对象,用于组织一类业务相关的对象
this.commandGroup = initGroupKey(group);
// commandKey默认是以类为为名称的
this.commandKey = initCommandKey(key, getClass());
this.properties = initCommandProperties(this.commandKey, propertiesStrategy, commandPropertiesDefaults);
//这个方法里定义了TheradPool里的关键字,默认以传入的commandGroup 的name做为key的名称
this.threadPoolKey = initThreadPoolKey(threadPoolKey, this.commandGroup, this.properties.executionIsolationThreadPoolKeyOverride().get());
this.metrics = initMetrics(metrics, this.commandGroup, this.threadPoolKey, this.commandKey, this.properties);
this.circuitBreaker = initCircuitBreaker(this.properties.circuitBreakerEnabled().get(), circuitBreaker, this.commandGroup, this.commandKey, this.properties, this.metrics);
//这里就是线程池对象啦。
this.threadPool = initThreadPool(threadPool, this.threadPoolKey, threadPoolPropertiesDefaults);
//Strategies from plugins
this.eventNotifier = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getEventNotifier();
this.concurrencyStrategy = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getConcurrencyStrategy();
HystrixMetricsPublisherFactory.createOrRetrievePublisherForCommand(this.commandKey, this.commandGroup, this.metrics, this.circuitBreaker, this.properties);
this.executionHook = initExecutionHook(executionHook);
this.requestCache = HystrixRequestCache.getInstance(this.commandKey, this.concurrencyStrategy);
this.currentRequestLog = initRequestLog(this.properties.requestLogEnabled().get(), this.concurrencyStrategy);
/* fallback semaphore override if applicable */
this.fallbackSemaphoreOverride = fallbackSemaphore;
/* execution semaphore override if applicable */
this.executionSemaphoreOverride = executionSemaphore;
}
/**
这个方法用于得到HystrixThreadPoolKey 对象, Hystrix内部有大量的Key对象,可以简单理解这些 Key都是相应对象的唯一标识。从代码里可以看出,默认情况下Hystrix采用的是commandGroup 的name做为Thread Pool的key值。
**/
private static HystrixThreadPoolKey initThreadPoolKey(HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixCommandGroupKey groupKey, String threadPoolKeyOverride) {
if (threadPoolKeyOverride == null) {
// we don't have a property overriding the value so use either HystrixThreadPoolKey or HystrixCommandGroup
if (threadPoolKey == null) {
/* use HystrixCommandGroup if HystrixThreadPoolKey is null */
return HystrixThreadPoolKey.Factory.asKey(groupKey.name());
} else {
return threadPoolKey;
}
} else {
// we have a property defining the thread-pool so use it instead
return HystrixThreadPoolKey.Factory.asKey(threadPoolKeyOverride);
}
}
/**
在这里将调用具体的构造线程池的方法。
**/
private static HystrixThreadPool initThreadPool(HystrixThreadPool fromConstructor, HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter threadPoolPropertiesDefaults) {
if (fromConstructor == null) {
// get the default implementation of HystrixThreadPool
return HystrixThreadPool.Factory.getInstance(threadPoolKey, threadPoolPropertiesDefaults);
} else {
return fromConstructor;
}
}从上面的代码分析我们知道线程池的构造最终会落到HystrixThreadPool.Factory这个类上面。这个类内存持有一个ConcurrentHashMap用于缓存线程池对象,当传入的HystrixThreadPoolKey已经构造过了相应的ThreadPool,将会直接从ConcurrentHashMap里返回已经生成的ThreadPool。如果传入的HystrixThreadPoolKey没有相应的ThreadPool,将构造新的ThreadPool并放入到ConcurrentHashMap这个缓存对象上。下面是关键代码:
static class Factory {
final static ConcurrentHashMap<String, HystrixThreadPool> threadPools = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, HystrixThreadPool>();
static HystrixThreadPool getInstance(HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter propertiesBuilder) {
// get the key to use instead of using the object itself so that if people forget to implement equals/hashcode things will still work
String key = threadPoolKey.name();
// this should find it for all but the first time
//这里从缓存取
HystrixThreadPool previouslyCached = threadPools.get(key);
if (previouslyCached != null) {
return previouslyCached;
}
// if we get here this is the first time so we need to initialize
//这里需要保证线程安全,加上了相应的锁
synchronized (HystrixThreadPool.class) {
if (!threadPools.containsKey(key)) {
//具体的线程池是由HystrixThreadPoolDefault进行构造的
threadPools.put(key, new HystrixThreadPoolDefault(threadPoolKey, propertiesBuilder));
}
}
return threadPools.get(key);
}
}
////////////////////////////////
//HystrixThreadPoolDefault 内部通过HystrixConcurrencyStrategy这个对象进行线程池的构造,里面根据传入的properties信息来构造线程池对象。 关键代码如下:
static class HystrixThreadPoolDefault implements HystrixThreadPool {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HystrixThreadPoolDefault.class);
private final HystrixThreadPoolProperties properties;
private final BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue;
private final ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool;
private final HystrixThreadPoolMetrics metrics;
private final int queueSize;
public HystrixThreadPoolDefault(HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter propertiesDefaults) {
this.properties = HystrixPropertiesFactory.getThreadPoolProperties(threadPoolKey, propertiesDefaults);
HystrixConcurrencyStrategy concurrencyStrategy = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getConcurrencyStrategy();
this.queueSize = properties.maxQueueSize().get();
this.metrics = HystrixThreadPoolMetrics.getInstance(threadPoolKey,
concurrencyStrategy.getThreadPool(threadPoolKey, properties),
properties);
this.threadPool = this.metrics.getThreadPool();
this.queue = this.threadPool.getQueue();
/* strategy: HystrixMetricsPublisherThreadPool */
HystrixMetricsPublisherFactory.createOrRetrievePublisherForThreadPool(threadPoolKey, this.metrics, this.properties);
}
}
///HystrixConcurrencyStrategy 类里我们可以看到采用的我们熟悉的ThreadPoolExecutor对象来构造线程池。 里面需要传入核心线程池的大小,最大线程数,队列等关键信息。
public ThreadPoolExecutor getThreadPool(final HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixThreadPoolProperties threadPoolProperties) {
final ThreadFactory threadFactory = getThreadFactory(threadPoolKey);
final boolean allowMaximumSizeToDivergeFromCoreSize = threadPoolProperties.getAllowMaximumSizeToDivergeFromCoreSize().get();
final int dynamicCoreSize = threadPoolProperties.coreSize().get();
final int keepAliveTime = threadPoolProperties.keepAliveTimeMinutes().get();
final int maxQueueSize = threadPoolProperties.maxQueueSize().get();
final BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue = getBlockingQueue(maxQueueSize);
if (allowMaximumSizeToDivergeFromCoreSize) {
final int dynamicMaximumSize = threadPoolProperties.maximumSize().get();
if (dynamicCoreSize > dynamicMaximumSize) {
logger.error("Hystrix ThreadPool configuration at startup for : " + threadPoolKey.name() + " is trying to set coreSize = " +
dynamicCoreSize + " and maximumSize = " + dynamicMaximumSize + ". Maximum size will be set to " +
dynamicCoreSize + ", the coreSize value, since it must be equal to or greater than the coreSize value");
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(dynamicCoreSize, dynamicCoreSize, keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.MINUTES, workQueue, threadFactory);
} else {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(dynamicCoreSize, dynamicMaximumSize, keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.MINUTES, workQueue, threadFactory);
}
} else {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(dynamicCoreSize, dynamicCoreSize, keepAliveTime, TimeUnit.MINUTES, workQueue, threadFactory);
}
}
熔断
//找到AbstractCommand类的initCircuitBreaker方法,这是熔断器的构造方法入口。首先判断是否打开了熔断器,只有在打开了熔断器后才会通过HystrixCircuitBreaker.Factory工厂新建一个熔断器,源码如下:
private static HystrixCircuitBreaker initCircuitBreaker(boolean enabled, HystrixCircuitBreaker fromConstructor,HystrixCommandGroupKey groupKey, HystrixCommandKey commandKey,HystrixCommandProperties properties, HystrixCommandMetrics metrics) {
if (enabled) {
if (fromConstructor == null) {
// get the default implementation of HystrixCircuitBreaker
return HystrixCircuitBreaker.Factory.getInstance(commandKey, groupKey, properties, metrics);
} else {
return fromConstructor;
}
} else {
return new NoOpCircuitBreaker();
}
}
//HystrixCircuitBreaker.Factory 类里对熔断器根据CommandKey进行了缓存,如果存在直接取缓存里的key,不存在则新建HystrixCircuitBreakerImpl对象用于熔断操作。源代码如下:
class Factory {
//circuitBreakersByCommand 是个ConcurrentHashMap, 这里缓存了系统的所有熔断器
private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, HystrixCircuitBreaker> circuitBreakersByCommand = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, HystrixCircuitBreaker>();
public static HystrixCircuitBreaker getInstance(HystrixCommandKey key, HystrixCommandGroupKey group, HystrixCommandProperties properties, HystrixCommandMetrics metrics) {
// this should find it for all but the first time
//先从缓存里取
HystrixCircuitBreaker previouslyCached = circuitBreakersByCommand.get(key.name());
if (previouslyCached != null) {
return previouslyCached;
}
// if we get here this is the first time so we need to initialize
// Create and add to the map ... use putIfAbsent to atomically handle the possible race-condition of
// 2 threads hitting this point at the same time and let ConcurrentHashMap provide us our thread-safety
// If 2 threads hit here only one will get added and the other will get a non-null response instead.
//取不到对象才会创建个HystrixCircuitBreakerImpl对象并放入缓存Map中
HystrixCircuitBreaker cbForCommand = circuitBreakersByCommand.putIfAbsent(key.name(), new HystrixCircuitBreakerImpl(key, group, properties, metrics));
if (cbForCommand == null) {
// this means the putIfAbsent step just created a new one so let's retrieve and return it
return circuitBreakersByCommand.get(key.name());
} else {
// this means a race occurred and while attempting to 'put' another one got there before
// and we instead retrieved it and will now return it
return cbForCommand;
}
}
/**
* Get the {@link HystrixCircuitBreaker} instance for a given {@link HystrixCommandKey} or null if none exists.
*
* @param key
* {@link HystrixCommandKey} of {@link HystrixCommand} instance requesting the {@link HystrixCircuitBreaker}
* @return {@link HystrixCircuitBreaker} for {@link HystrixCommandKey}
*/
public static HystrixCircuitBreaker getInstance(HystrixCommandKey key) {
return circuitBreakersByCommand.get(key.name());
}
/**
* Clears all circuit breakers. If new requests come in instances will be recreated.
*/
/* package */static void reset() {
circuitBreakersByCommand.clear();
}
}
//HystrixCircuitBreakerImpl 这个类里定义了一个状态变量,断路由有三种状态 ,分别为关闭,打开,半开状态。重点关注下allowRequest方法,在allowRequest里首先判断forceOpen属性是否打开,如果打开则不允许有请求进入,然后forceClosed属性,如果这个属性为true,刚对所有的求求放行,相当于熔断器不起作用。之后就是状态判断了。isAfterSleepWindow()方法用于放行超过了指定时间后的流量,
class HystrixCircuitBreakerImpl implements HystrixCircuitBreaker {
private final HystrixCommandProperties properties;
private final HystrixCommandMetrics metrics;
//三种状态通过枚举来定义
enum Status {
CLOSED, OPEN, HALF_OPEN;
}
//状态变时,默认是关闭的状态
private final AtomicReference<Status> status = new AtomicReference<Status>(Status.CLOSED);
//最后一次访问的时间,用于试探请求是否恢复
private final AtomicLong circuitOpened = new AtomicLong(-1);
private final AtomicReference<Subscription> activeSubscription = new AtomicReference<Subscription>(null);
protected HystrixCircuitBreakerImpl(HystrixCommandKey key, HystrixCommandGroupKey commandGroup, final HystrixCommandProperties properties, HystrixCommandMetrics metrics) {
this.properties = properties;
this.metrics = metrics;
//On a timer, this will set the circuit between OPEN/CLOSED as command executions occur
Subscription s = subscribeToStream();
activeSubscription.set(s);
}
private Subscription subscribeToStream() {
/*
* This stream will recalculate the OPEN/CLOSED status on every onNext from the health stream
*/
return metrics.getHealthCountsStream()
.observe()
.subscribe(new Subscriber<HealthCounts>() {
@Override
public void onCompleted() {
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
}
@Override
public void onNext(HealthCounts hc) {
// check if we are past the statisticalWindowVolumeThreshold
if (hc.getTotalRequests() < properties.circuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold().get()) {
// we are not past the minimum volume threshold for the stat window,
// so no change to circuit status.
// if it was CLOSED, it stays CLOSED
// if it was half-open, we need to wait for a successful command execution
// if it was open, we need to wait for sleep window to elapse
} else {
if (hc.getErrorPercentage() < properties.circuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage().get()) {
//we are not past the minimum error threshold for the stat window,
// so no change to circuit status.
// if it was CLOSED, it stays CLOSED
// if it was half-open, we need to wait for a successful command execution
// if it was open, we need to wait for sleep window to elapse
} else {
// our failure rate is too high, we need to set the state to OPEN
if (status.compareAndSet(Status.CLOSED, Status.OPEN)) {
circuitOpened.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
}
}
});
}
//将熔断器置于关闭状态,并重置统计数据
@Override
public void markSuccess() {
if (status.compareAndSet(Status.HALF_OPEN, Status.CLOSED)) {
//This thread wins the race to close the circuit - it resets the stream to start it over from 0
metrics.resetStream();
Subscription previousSubscription = activeSubscription.get();
if (previousSubscription != null) {
previousSubscription.unsubscribe();
}
Subscription newSubscription = subscribeToStream();
activeSubscription.set(newSubscription);
circuitOpened.set(-1L);
}
}
//将熔断器置于打开状态
@Override
public void markNonSuccess() {
if (status.compareAndSet(Status.HALF_OPEN, Status.OPEN)) {
//This thread wins the race to re-open the circuit - it resets the start time for the sleep window
circuitOpened.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
//用于判断熔断器是否打开
@Override
public boolean isOpen() {
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceOpen().get()) {
return true;
}
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceClosed().get()) {
return false;
}
return circuitOpened.get() >= 0;
}
//用于判断是否放行流量
@Override
public boolean allowRequest() {
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceOpen().get()) {
return false;
}
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceClosed().get()) {
return true;
}
//第一次请求肯定就放行了
if (circuitOpened.get() == -1) {
return true;
} else {
//半开状态将不放行
if (status.get().equals(Status.HALF_OPEN)) {
return false;
} else {
return isAfterSleepWindow();
}
}
}
//根据当前时间与最后一次请求的时候进行比较,当超过了设置的SleepWindowInMilliseconds,将放行请求用于试探服务访问是否OK
private boolean isAfterSleepWindow() {
final long circuitOpenTime = circuitOpened.get();
final long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
final long sleepWindowTime = properties.circuitBreakerSleepWindowInMilliseconds().get();
return currentTime > circuitOpenTime + sleepWindowTime;
}
//用于试探服务是否OK的方法
@Override
public boolean attemptExecution() {
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceOpen().get()) {
return false;
}
if (properties.circuitBreakerForceClosed().get()) {
return true;
}
if (circuitOpened.get() == -1) {
return true;
} else {
if (isAfterSleepWindow()) {
//only the first request after sleep window should execute
//if the executing command succeeds, the status will transition to CLOSED
//if the executing command fails, the status will transition to OPEN
//if the executing command gets unsubscribed, the status will transition to OPEN
if (status.compareAndSet(Status.OPEN, Status.HALF_OPEN)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
配置参数
#Execution相关的属性的配置
#隔离策略,默认是Thread, 可选Thread| Semaphor
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.strategy
#命令执行超时时 间,默认1000ms
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds
# 执行是否启用超时,默认启用true
hystrix.command.default.execution.timeout.enabled
# 发生超时是是否中断, 默认true
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.thread.interruptOnTimeout
# 最大并发请求 数,默认10,该参数当使用ExecutionIsolationStrategy.SEMAPHORE策略时才有效。如果达到最大并发请求 数,请求会被拒绝。理论上选择semaphore size的原则和选择thread size一致,但选用semaphore时每次执行 的单元要比较小且执行速度快(ms级别),否则的话应该用thread。 semaphore应该占整个容器(tomcat)的线程池的一小部分。 Fallback相关的属性 这些参数可以应用于Hystrix的THREAD和SEMAPHORE策略
hystrix.command.default.execution.isolation.semaphore.maxConcurrentRequests
# 如果并发数达到 该设置值,请求会被拒绝和抛出异常并且fallback不会被调用。默认10
hystrix.command.default.fallback.isolation.semaphore.maxConcurrentRequests
# 当执行失败或者请求被拒绝,是否会尝试调用
hystrix.command.default.fallback.enabled
# Circuit Breaker相关的属性
#用来跟踪circuit的健康性,如果未达标则让request短路。默认true
hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.enabled
# 一个rolling window内最小的请 求数。如果设为20,那么当一个rolling window的时间内(比如说1个rolling window是10秒)收到19个请求, 即使19个请求都失败,也不会触发circuit break。默认20
hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold
# 触发短路的时间值,当该值设 为5000时,则当触发circuit break后的5000毫秒内都会拒绝request,也就是5000毫秒后才会关闭circuit。 默认5000
hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds
# 错误比率阀值,如果错误率>=该 值,circuit会被打开,并短路所有请求触发fallback。默认50
hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage
# 强制打开熔断器,如果打开这个开关,那么拒绝所 有request,默认false
hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.forceOpen
# 强制关闭熔断器 如果这个开关打开,circuit将 一直关闭且忽略circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage
hystrix.command.default.circuitBreaker.forceClosed
# Metrics相关参数
#设置统计的时间窗口值的,毫秒 值,circuit break 的打开会根据1个rolling window的统计来计算。若rolling window被设为10000毫秒, 则rolling window会被分成n个buckets,每个bucket包含success,failure,timeout,rejection的次数 的统计信息。默认10000
hystrix.command.default.metrics.rollingStats.timeInMilliseconds
# 设置一个rolling window被划分的数 量,若numBuckets=10,rolling window=10000,那么一个bucket的时间即1秒。必须符合rolling window % numberBuckets == 0。默认10
hystrix.command.default.metrics.rollingStats.numBuckets
# 执行时是否enable指标的计算和跟踪, 默认true
hystrix.command.default.metrics.rollingPercentile.enabled
# 设置rolling percentile window的时间,默认60000
hystrix.command.default.metrics.rollingPercentile.timeInMilliseconds
# 设置rolling percentile window的numberBuckets。逻辑同上。默认6
hystrix.command.default.metrics.rollingPercentile.numBuckets
# 如果bucket size=100,window =10s,若这10s里有500次执行,只有最后100次执行会被统计到bucket里去。增加该值会增加内存开销以及排序 的开销。默认100
hystrix.command.default.metrics.rollingPercentile.bucketSize
# 记录health 快照(用 来统计成功和错误绿)的间隔,默认500ms
hystrix.command.default.metrics.healthSnapshot.intervalInMilliseconds
#Request Context 相关参数
# 默认true,需要重载getCacheKey(),返回null时不 缓存
hystrix.command.default.requestCache.enabled
# 记录日志到HystrixRequestLog,默认true
hystrix.command.default.requestLog.enabled
#Collapser Properties 相关参数
# 单次批处理的最大请求数,达到该数量触发批处理,默认 Integer.MAX_VALU
hystrix.collapser.default.maxRequestsInBatch
# 触发批处理的延迟,也可以为创建批处理的时间 +该值,默认10
hystrix.collapser.default.timerDelayInMilliseconds
# 是否对HystrixCollapser.execute() and HystrixCollapser.queue()的cache,默认true
hystrix.collapser.default.requestCache.enabled
#ThreadPool 相关参数
#线程数默认值10适用于大部分情况(有时可以设置得更小),如果需要设置得更大,那有个基本得公式可以 follow: requests per second at peak when healthy × 99th percentile latency in seconds + some breathing room 每秒最大支撑的请求数 (99%平均响应时间 + 缓存值) 比如:每秒能处理1000个请求,99%的请求响应时间是60ms,那么公式是: 1000 (0.060+0.012)
#基本得原则时保持线程池尽可能小,他主要是为了释放压力,防止资源被阻塞。 当一切都是正常的时候,线程池一般仅会有1到2个线程激活来提供服务
# 并发执行的最大线程数,默认10
hystrix.threadpool.default.coreSize
# BlockingQueue的最大队列数,当设为-1,会使用SynchronousQueue,值为正时使用LinkedBlcokingQueue。该设置只会在初始化时有效,之后不能修改threadpool的queue size,除非reinitialising thread executor。默认-1。
hystrix.threadpool.default.maxQueueSize
# 即使maxQueueSize没有达到,达到 queueSizeRejectionThreshold该值后,请求也会被拒绝。因为maxQueueSize不能被动态修改,这个参数将允 许我们动态设置该值。if maxQueueSize == -1,该字段将不起作用 hystrix.threadpool.default.keepAliveTimeMinutes 如果corePoolSize和maxPoolSize设成一样(默认 实现)该设置无效。如果通过plugin(https://github.com/Netflix/Hystrix/wiki/Plugins)使用自定义 实现,该设置才有用,默认1.
hystrix.threadpool.default.queueSizeRejectionThreshold
#线程池统计指标的时间,默 认10000
hystrix.threadpool.default.metrics.rollingStats.timeInMilliseconds
# 将rolling window划分为n个 buckets,默认10
hystrix.threadpool.default.metrics.rollingStats.numBuckets