01nio
NIO
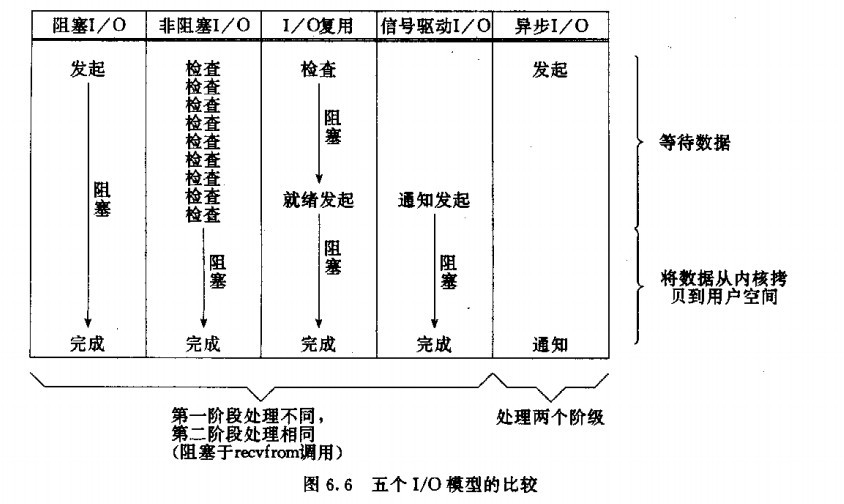
5种IO模型
- 阻塞I/O(blocking I/O)
- 非阻塞I/O (nonblocking I/O)
- I/O复用(select ,poll,epoll) (I/O multiplexing)
- 信号驱动I/O (signal driven I/O (SIGIO))
- 异步I/O (asynchronous I/O (the POSIX aio_functions))
NIO和BIO区别
BIO:面向流,阻塞式
NIO:面向缓冲区,非阻塞式,多路复用,基于事件驱动思想
NIO中selector是阻塞的,当然也有selectNow,和超时的方法,非阻塞是每个IO不是阻塞的。
BIO
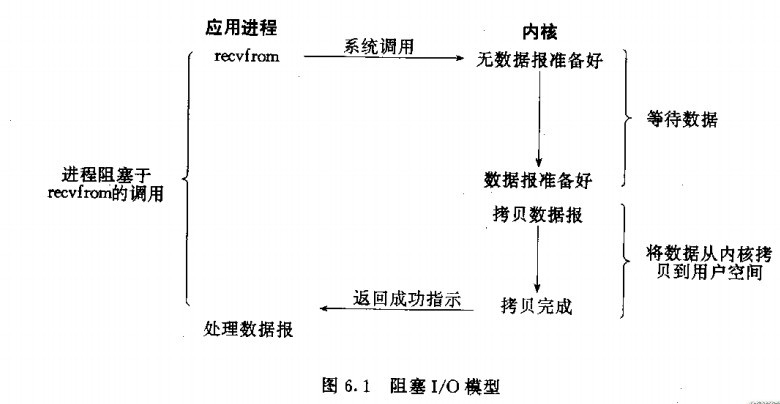
应用程序想要读取数据就会调用recvfrom,而recvfrom会通知OS来执行,OS就会判断数据报是否准备好(比如判断是否收到了一个完整的UDP报文,如果收到UDP报文不完整,那么就继续等待)。当数据包准备好了之后,OS就会将数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间(因为我们的用户程序只能获取用户空间的内存,无法直接获取内核空间的内存)。拷贝完成之后socket.read()就会解除阻塞,并得到read的结果。
会有两个地方阻塞
- OS等待数据报准备好。
- 将数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间。
public class ServerTcpSocket {
static byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
try {
// 1.创建一个ServerSocket连接
final ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket();
// 2.绑定端口号
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 3.当前线程放弃cpu资源等待获取数据
System.out.println("等待获取数据...");
while (true) {
//阻塞!!!!!!!!!
final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("获取到数据...");
// 4.读取数据
//阻塞!!!!!!!!!!!!
int read = socket.getInputStream().read(bytes);
String result = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
});
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}Non-Blocking IO
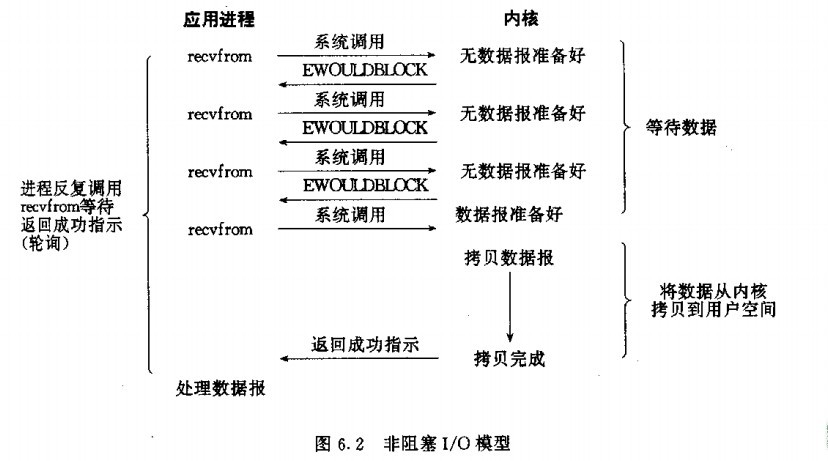
非阻塞I/O 不管是否有获取到数据,都会立马获取结果,如果没有获取数据的话、那么就不间断的循环重试,但是我们整个应用程序不会实现阻塞,线程不会睡眠。
public class NoBlockServer {
static ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 1.创建一个ServerSocketChannel连接
final ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 2.绑定端口号
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 设置为非阻塞式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
while(true){
// 非阻塞式
//没有连接就返回null
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if (socketChannel != null) {
//阻塞
int j = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
if (j > 0) {
byte[] bytes = Arrays.copyOf(byteBuffer.array(), byteBuffer.limit());
System.out.println("获取到数据" + new String(bytes));
}
}
System.out.println("程序执行完毕..");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}NIO的多路复用
Non-Blocking IO+I/O multiplexing
复用I/O:主要是select和epoll;对一个IO端口,两次调用,两次返回,比阻塞IO并没有什么优越性;关键是能实现同时对多个IO端口进行监听; I/O复用模型会用到select、poll、epoll函数,这几个函数也会使进程阻塞,但是和阻塞I/O所不同的的,这两个函数可以同时阻塞多个I/O操作。而且可以同时对多个读操作,多个写操作的I/O函数进行检测,直到有数据可读或可写时,才真正调用I/O操作函数。
flip()方法
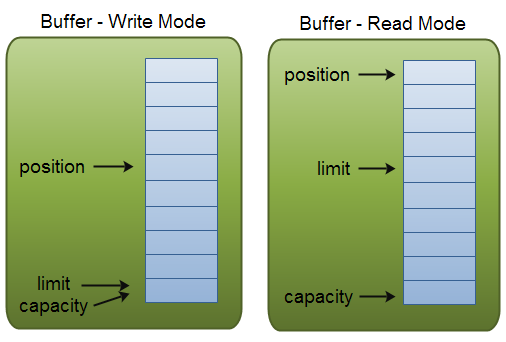
- 缓冲区本质上是一块可以写入数据,然后可以从中读取数据的内存。这块内存被包装成NIO Buffer对象,并提供了一组方法,用来方便的访问该块内存。为了理解Buffer的工作原理,需要熟悉它的三个属性:
- capacity
- position
- limit
- position和limit的含义取决于Buffer处在读模式还是写模式。不管Buffer处在什么模式,capacity的含义总是一样的。
- capacity
- 作为一个内存块,Buffer有一个固定的大小值,也叫“capacity”.你只能往里写capacity个byte、long,char等类型。一旦Buffer满了,需要将其清空(通过读数据或者清除数据)才能继续写数据往里写数据。
- position
- 当你写数据到Buffer中时,position表示当前的位置。初始的position值为0.当一个byte、long等数据写到Buffer后, position会向前移动到下一个可插入数据的Buffer单元。position最大可为capacity – 1.
- 当读取数据时,也是从某个特定位置读。当将Buffer从写模式切换到读模式,position会被重置为0. 当从Buffer的position处读取数据时,position向前移动到下一个可读的位置。
- limit
- 在写模式下,Buffer的limit表示你最多能往Buffer里写多少数据。 写模式下,limit等于Buffer的capacity。
- 当切换Buffer到读模式时, limit表示你最多能读到多少数据。因此,当切换Buffer到读模式时,limit会被设置成写模式下的position值。换句话说,你能读到之前写入的所有数据(limit被设置成已写数据的数量,这个值在写模式下就是position)
public class Server {
// 缓冲区的大小
private final static int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
// 缓冲区
private ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER_SIZE);
// Server监听的端口号
// private final static int PORT = 8888;
// 选择器
private Selector selector = null;
// 初始化工作
public void init(int port) throws IOException {
System.out.println("============ Listening On Port : " + port + "============");
// 打开服务器套接字通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 设置为非阻塞状态
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 获取通道相关联的套接字
ServerSocket serverSocket = serverSocketChannel.socket();
// 绑定端口号
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
// 打开一个选择器
selector = Selector.open();
// 服务器套接字注册到Selector中 并指定Selector监控连接事件
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}
public void listen() throws IOException {
while (true) {
// 开启选择
int readyChannels = selector.select(); // 没有通道就绪 一直阻塞 返回已经就绪通道的数目(有可能为0)
if (readyChannels == 0) {
continue;
}
// 返回已选择键的集合
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
// 遍历键 并检查键对应的通道里注册的就绪事件
Iterator iterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// SelectionKey封装了一个通道和选择器的注册关系
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) iterator.next();
handleKey(key);
// Selector不会移除SelectionKey 处理完了手动移除
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
// 处理SelectionKey
private void handleKey(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
// 是否有连接进来
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();// 获取通道 转化为要处理的类型
SocketChannel socketChannel = server.accept();
// SocketChannel通道的可读事件注册到Selector中
registerChannel(selector, socketChannel, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// 连接成功 向Client打个招呼
if (socketChannel.isConnected()) {
buffer.clear();
buffer.put("I am Server...".getBytes());
buffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(buffer);
}
}
// 通道的可读事件就绪
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
buffer.clear(); // 清空缓冲区
// 读取数据
int len = 0;
while ((len = socketChannel.read(buffer)) > 0) {
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println("Server读取的数据:" + new String(buffer.array(), 0, len));
}
}
if (len < 0) {
// 非法的SelectionKey 关闭Channel
socketChannel.close();
}
// SocketChannel通道的可写事件注册到Selector中
registerChannel(selector, socketChannel, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
// 通道的可写事件就绪
if (key.isWritable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
buffer.clear(); // 清空缓冲区
// 准备发送的数据
String message_from_server = "Hello,Client... " + socketChannel.getLocalAddress();
buffer.put(message_from_server.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(buffer);
System.out.println("Server发送的数据:" + message_from_server);
// SocketChannel通道的可写事件注册到Selector中
registerChannel(selector, socketChannel, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
// 注册通道到指定Selector上
private void registerChannel(Selector selector, SelectableChannel channel, int ops) throws IOException {
if (channel == null) {
return;
}
channel.configureBlocking(false);
// 注册通道
channel.register(selector, ops);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Server server = new Server();
server.init(8888);
server.listen();
}
}
public class Client {
// 缓冲区的大小
private final static int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
// 缓冲区
private ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER_SIZE);
// 选择器
private Selector selector = null;
private final static int PORT = 8888;
// 初始化工作
public void init(String address) throws IOException {
// 打开客户端套接字通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
// 设置为非阻塞状态
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 打开选择器
selector = Selector.open();
// 注册
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
// 发起连接
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(address, PORT));
}
public void connect() throws IOException {
while (true) {
//阻塞
int readyChannels = selector.select();
if (readyChannels == 0) {
continue;
}
// 返回已选择键的集合
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
// 遍历键 并检查键对应的通道里注册的就绪事件
Iterator iterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// SelectionKey封装了一个通道和选择器的注册关系
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) iterator.next();
handleKey(key);
// Selector不会移除SelectionKey 处理完了手动移除
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
// 处理SelectionKey
private void handleKey(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
// 是否可连接
if (key.isConnectable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
// 完成连接
if(socketChannel.isConnectionPending()) {
socketChannel.finishConnect();
System.out.println("连接成功...");
// 发送数据给Server
String message_to_server = "Hello,Server...";
buffer.clear();
buffer.put(message_to_server.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(buffer);
System.out.println("Client发送的数据:" + message_to_server);
registerChannel(selector, socketChannel, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else {
System.exit(1); // 连接失败 退出
}
}
// 通道的可读事件就绪
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
buffer.clear(); // 清空缓冲区
// 读取数据
int len = 0;
while ((len = socketChannel.read(buffer)) > 0) {
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println("Client读取的数据:" + new String(buffer.array(), 0, len));
}
}
if (len < 0) {
// 非法的SelectionKey 关闭Channel
socketChannel.close();
}
// SocketChannel通道的可写事件注册到Selector中
registerChannel(selector, socketChannel, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
// 通道的可写事件就绪
if (key.isWritable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
buffer.clear(); // 清空缓冲区
// 准备发送的数据
String message_from_server = "Hello,Server... " + socketChannel.getLocalAddress();
buffer.put(message_from_server.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(buffer);
System.out.println("Client发送的数据:" + message_from_server);
// SocketChannel通道的可写事件注册到Selector中
registerChannel(selector, socketChannel, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
// 注册通道到指定Selector上
private void registerChannel(Selector selector, SelectableChannel channel, int ops) throws IOException {
if (channel == null) {
return;
}
channel.configureBlocking(false);
// 注册通道
channel.register(selector, ops);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Client client = new Client();
client.init("localhost");
client.connect();
}
}01nio
https://jiajun.xyz/2021/05/16/java/netty/nio/01nio/