07tools
本文最后更新于 2026-01-05 09:44:55
Tools
Tool calling(也称为function calling)是AI应用中常见的一种模式,允许模型与一组API或工具交互,增强其能力。
工具主要用于:
信息检索。这类工具可用于从外部来源检索信息,如数据库、网络服务、文件系统或网页搜索引擎。目标是增强模型的知识,使其能够回答那些原本无法回答的问题。因此,它们可以在检索增强生成(RAG)场景中使用。例如,工具可以用来检索某一地点的当前天气、获取最新新闻文章,或查询数据库中的特定记录。
采取行动。该类工具可用于在软件系统中执行作,如发送电子邮件、在数据库中创建新记录、提交表单或触发工作流程。目标是自动化那些原本需要人工干预或显式编程的任务。例如,工具可用于为与聊天机器人互动的客户预订航班、填写网页表单。
工具调用逻辑由客户端应用程序提供。模型只能请求工具调用并提供输入参数,而应用程序负责从输入参数执行工具调用并返回结果
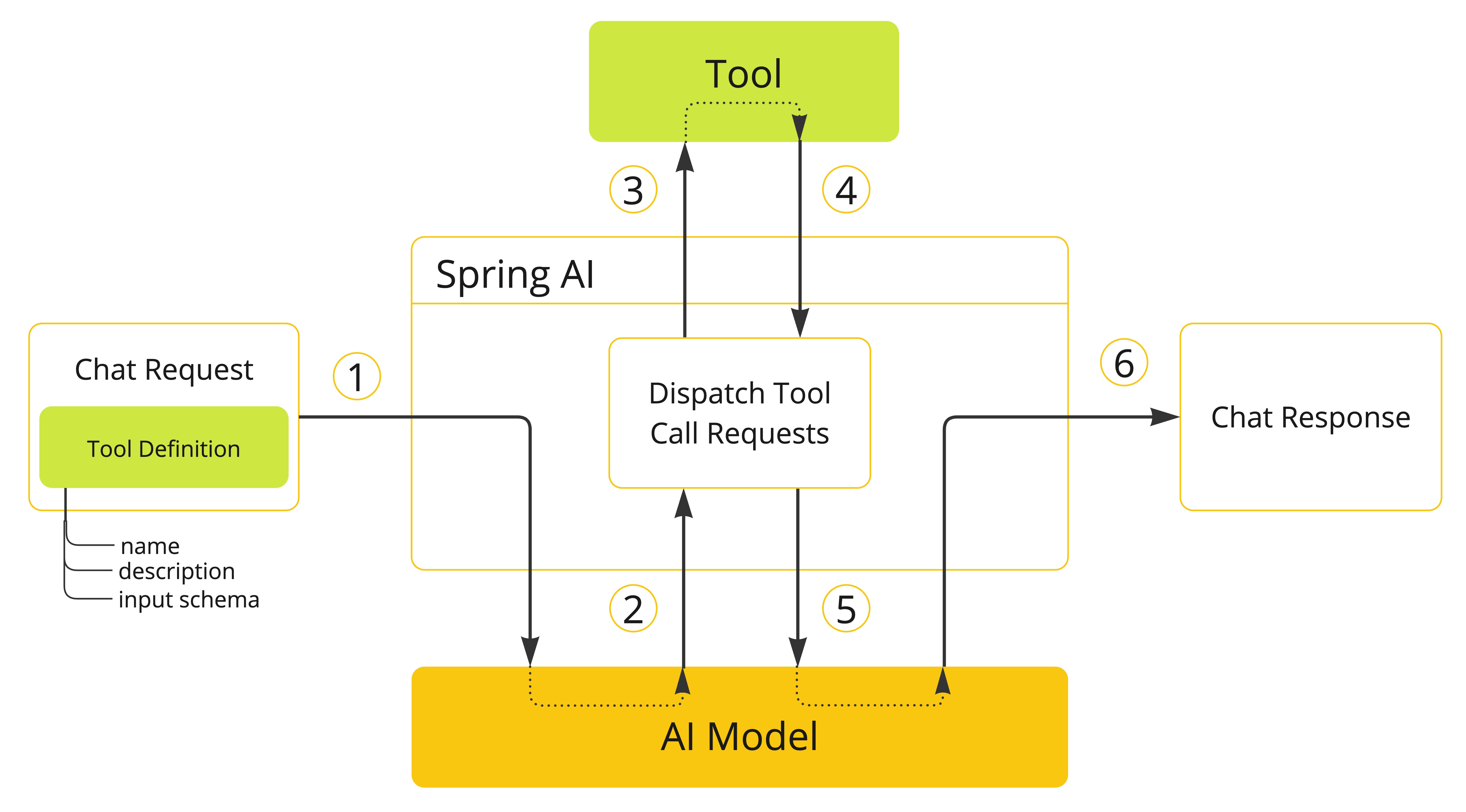
方法作为Tools定义及使用
注解定义
@Tool(description = "根据地址 获取天气信息")
public String getWeatherInfo(
@ToolParam(required = true,description = "地址") String address){
return address+"的天气信息是 晴天";
}@Tool参数:
- name: 工具的名字。如果未提供,将使用方法名称。AI模型在调用工具时使用这个名称来识别它。该名称必须是唯一的。
- description: 工具的描述,模型可以用来理解何时以及如何调用该工具。如果未提供,方法名称将作为工具描述使用。
- returnDirect: 是否直接将结果返回值client
- resultConverter: 默认
ToolCallResultConverter用于将工具调用的结果转换为String对象以发送回AI模型。
@ToolParam:
- description: 参数的描述,模型可以使用它来更好地理解如何使用它。例如,参数应该采用什么格式,允许使用什么值,等等。
- required: 参数是必需的还是可选的。默认情况下,所有参数都是必需的。
向chatClient添加tools
ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What day is tomorrow?")
.tools(new DateTimeTools())
.call()
.content();在底层,ChatClient将从工具类实例中的每个@Tool注解方法生成一个ToolCallback
向chatClient添加默认tools
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultTools(new DateTimeTools())
.build();向chatClient添加toolCallback
MethodToolCallback.Builder
- toolDefinition: 定义工具名称、描述和输入模式的ToolDefinition实例。您可以使用ToolDefinition来构建它。构建器类。必需的。
- name: 工具的名称。如果没有提供,则使用方法名。
- description: 工具的描述,模型可以使用它来理解何时以及如何调用工具
- inputSchema: 工具输入参数的JSON模式。如果没有提供,模式将根据方法参数自动生成。可以使用@ToolParam注释来提供关于输入参数的附加信息
- toolMetadata: 定义了额外的设置,比如是否应该将结果直接返回给客户端
- returnDirect: 工具结果是否应该直接返回给客户端或传递回模型。
- toolMethod: 表示工具方法的Method实例。必需的。
- toolObject: 包含工具方法的对象实例。如果方法是静态的,则可以省略此参数。
- toolCallResultConverter: ToolCallResultConverter实例,用于将工具调用的结果转换为String对象以发送回AI模型。如果没有提供,将使用默认的转换器(DefaultToolCallResultConverter)。
/**
ToolDefinition toolDefinition = ToolDefinition.builder()
.name("currentWeather")
.description("Get the weather in location")
// 定义input schema
.inputSchema("""
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["C", "F"]
}
},
"required": ["location", "unit"]
}
""")
.build();
// 根据方法生成ToolDefinition
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getCurrentDateTime");
ToolDefinition toolDefinition = ToolDefinition.from(method);
**/
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getCurrentDateTime");
ToolCallback toolCallback = MethodToolCallback.builder()
.toolDefinition(ToolDefinitions.builder(method)
.description("Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
.build())
.toolMethod(method)
.toolObject(new DateTimeTools())
.build();
ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What day is tomorrow?")
.toolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.call()
.content();向chatClient添加默认toolCallback
ChatModel chatModel = ...
ToolCallback toolCallback = ...
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultToolCallbacks(toolCallback)
.build();限制:
以下类型目前不支持作为用作工具的参数的参数或返回类型:
Optional- 异步类型(例如
CompletableFuture、Future) - 响应式类型(例如
Flow、Mono、Flux) - 函数式类型(例如
Function、Supplier、Consumer)。
函数作为Tools定义及使用
可以通过编程方式构建FunctionToolCallback将函数式类型(Function、Supplier、Consumer或BiFunction)转变为工具。
定义
public class WeatherService implements Function<WeatherRequest, WeatherResponse> {
public WeatherResponse apply(WeatherRequest request) {
return new WeatherResponse(30.0, Unit.C);
}
}
public enum Unit { C, F }
public record WeatherRequest(String location, Unit unit) {}
public record WeatherResponse(double temp, Unit unit) {}定义toolCallback
FunctionToolCallback.Builder
name:工具的名称。如果没有提供,则使用方法名。toolFunction:表示工具方法的功能对象(Function、Supplier、Consumer或BiFunction)。必需。description:工具的描述,模型可用于理解何时以及如何调用该工具。如果未提供,则使用方法名作为工具描述。但是,强烈建议提供详细描述,因为这对于模型理解工具的用途以及如何使用至关重要。未能提供良好的描述可能导致模型在该使用时未使用工具或使用不正确。inputType:函数输入的类型。必需。inputSchema:工具输入参数的JSON架构。如果未提供,将根据inputType自动生成架构。您可以使用@ToolParam注解提供有关输入参数的附加信息,例如描述或参数是必需还是可选。toolMetadata:定义了额外的设置,比如是否应该将结果直接返回给客户端- returnDirect: 工具结果是否应该直接返回给客户端或传递回模型。
toolCallResultConverter:用于将工具调用结果转换为要发送回AI模型的String对象的ToolCallResultConverter实例。如果未提供,则将使用默认转换器(DefaultToolCallResultConverter)。
ToolCallback toolCallback = FunctionToolCallback
.builder("currentWeather", new WeatherService())
.description("Get the weather in location")
.inputType(WeatherRequest.class)
.build();@Bean
将工具定义为Spring bean,并让Spring AI在运行时使用ToolCallbackResolver接口(通过SpringBeanToolCallbackResolver实现)动态解析它们。此选项使您能够将任何Function、Supplier、Consumer或BiFunction bean用作工具。bean名称将用作工具名称,Spring Framework的@Description注解可用于提供工具的描述,供模型理解何时以及如何调用该工具。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
class WeatherTools {
WeatherService weatherService = new WeatherService();
@Bean
@Description("Get the weather in location")
Function<WeatherRequest, WeatherResponse> currentWeather() {
return weatherService;
}
}通过bean name 引入
ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("What's the weather like in Copenhagen?")
.toolNames("currentWeather")
.call()
.content();Tool Context 上下文
Spring AI支持通过ToolContext API向工具传递额外的上下文信息。此功能允许提供额外的、用户提供的数据,这些数据可以在工具执行期间与AI模型传递的工具参数一起使用。
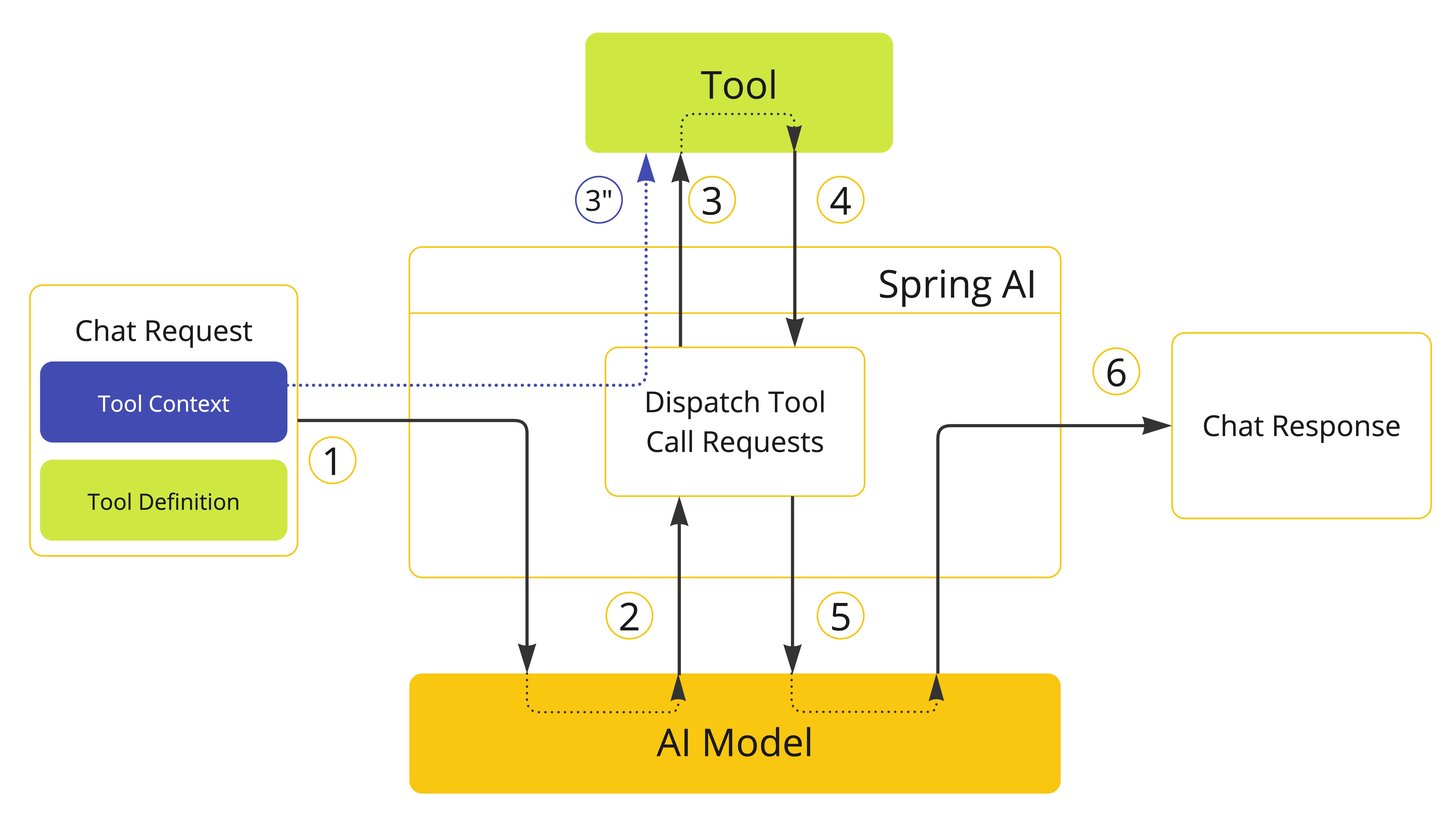
class CustomerTools {
@Tool(description = "Retrieve customer information")
Customer getCustomerInfo(Long id, ToolContext toolContext) {
return customerRepository.findById(id, toolContext.getContext().get("tenantId"));
}
}ChatModel chatModel = ...
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("Tell me more about the customer with ID 42")
.tools(new CustomerTools())
.toolContext(Map.of("tenantId", "acme"))
.call()
.content();
System.out.println(response);异常处理
当工具调用失败时,异常会作为ToolExecutionException传播,可以捕获该异常以处理错误。ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor可用于处理ToolExecutionException
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor {
/**
* 将工具抛出的异常转换为可以发送回AI模型的String,或抛出要由调用者处理的异常。
*/
String process(ToolExecutionException exception);
}@Bean
ToolExecutionExceptionProcessor toolExecutionExceptionProcessor() {
return new DefaultToolExecutionExceptionProcessor(true);
}如果定义了自己的ToolCallback实现,请确保在call()方法中作为工具执行逻辑的一部分发生错误时抛出ToolExecutionException。
捕获LLM工具调用推理
import org.springframework.ai.tool.annotation.ToolParam;
public record AgentThinking(
@ToolParam(description = "Your step-by-step reasoning for why you're calling this tool and what you expect", required = true)
String innerThought,
@ToolParam(description = "Confidence level (low, medium, high) in this tool choice", required = false)
String confidence,
@ToolParam(description = "Key insights to remember for future interactions", required = true)
List<String> memoryNotes
) {}
////////////////////////////////////////////
import org.springframework.ai.tool.augment.AugmentedToolCallbackProvider;
// Your existing tool defined using Spring AI @Tool annotation
public class WeatherTool {
@Tool(description = "Get the current weather for a given location")
public String weather(String location) {
return "The current weather in " + location + " is sunny with a temperature of 25°C.";
}
}
// Wrap with augmented arguments
AugmentedToolCallbackProvider<AgentThinking> provider =
AugmentedToolCallbackProvider.<AgentThinking>builder()
.toolObject(new WeatherTool())
.argumentType(AgentThinking.class)
.argumentConsumer(event -> {
// Access the augmented arguments via event.arguments()
AgentThinking thinking = event.arguments();
// Log the LLM's reasoning - great for debugging and observability
log.info("Tool: {}, LLM Reasoning: {}, Confidence: {}",
event.toolDefinition().name(), thinking.innerThought(), thinking.confidence());
// Store insights in memory for future context
thinking.memoryNotes().forEach(note ->
memorySystem.store(note)
);
})
.build();
// Use with Spring AI ChatClient
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultToolCallbacks(provider)
.build();
What the LLM Sees
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The location to get weather for"
},
"innerThought": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Your step-by-step reasoning for why you're calling this tool and what you expect"
},
"confidence": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Confidence level (low, medium, high) in this tool choice"
},
"memoryNotes": {
"type": "array",
"items": { "type": "string" },
"description": "Key insights to remember for future interactions"
}
},
"required": ["location", "innerThought", "memoryNotes"]
}LLM Response with Reasoning
{
"location": "Amsterdam",
"innerThought": "The user is asking about what to wear in Amsterdam today. I need to check the current weather conditions to provide appropriate clothing recommendations.",
"confidence": "high",
"memoryNotes": [
"User is planning an outing in Amsterdam",
"May need follow-up with specific activity questions"
]
}Your consumer receives the AgentThinking record with all the reasoning, while the original tool receives only {"location": "Amsterdam"}.
Include Reasoning in Final Response(Optional)
public record ResponseWithReasoning(
String response,
AgentThinking thinking
) {}
var answer = chatClient
.prompt("What should I wear in Amsterdam today?")
.call()
.entity(ResponseWithReasoning.class); // structured response
// Access both the response and the reasoning
System.out.println("Answer: " + answer.response());
System.out.println("Reasoning: " + answer.thinking().innerThought());