08MCP
本文最后更新于 2026-01-13 10:37:54
MCP(Model Context Protocol)
MCP Client
负责建立和管理与MCP服务器的连接。它实现了协议的客户端
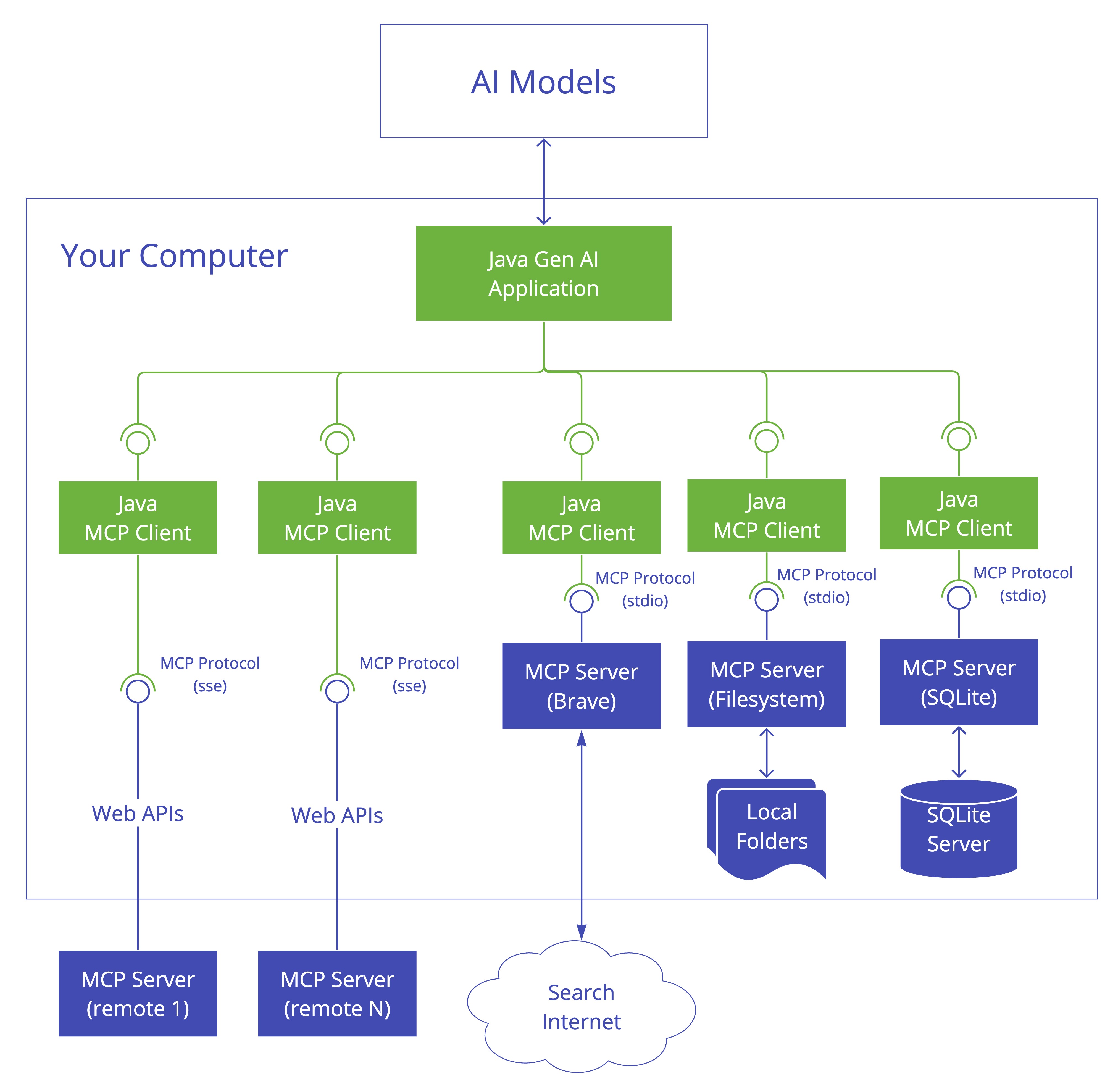
MCP Server
客户端提供工具、资源和功能
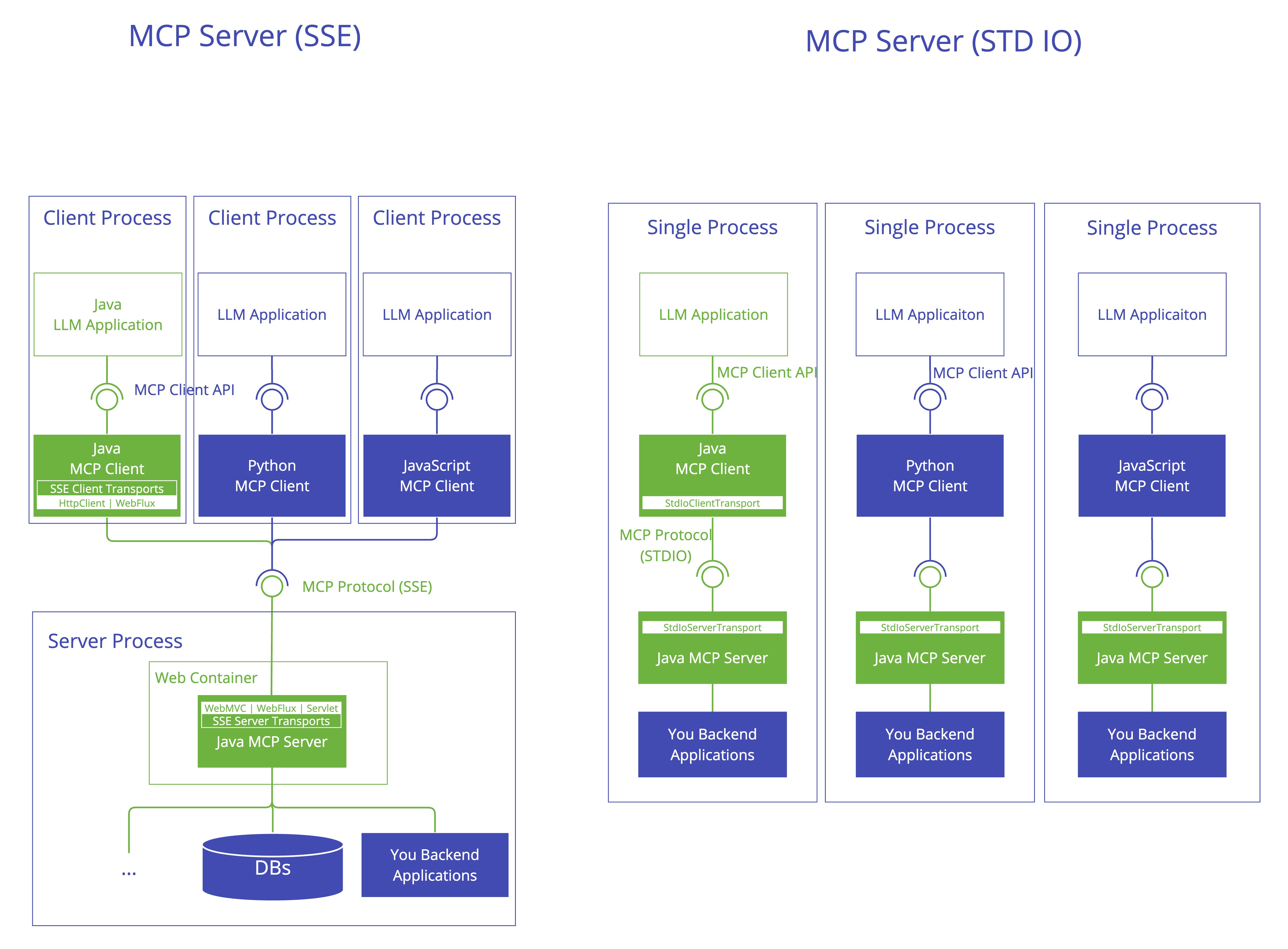
Spring AI MCP 集成
Client Starters
spring-ai-starter-mcp-client- Core starter providing STDIO and HTTP-based SSE supportspring-ai-starter-mcp-client-webflux- WebFlux-based SSE transport implementation
标准启动器通过STDIO(进程内)和/或SSE(远程)传输同时连接到一个或多个MCP服务器。SSE连接使用基于httpclient的传输实现。
每个到MCP服务器的连接都会创建一个新的MCP客户端实例。
您可以选择同步或异步MCP客户端(注意:不能混合同步和异步客户端)。
对于生产部署,我们建议使用基于webflux的SSE连接。
配置参数
spring.ai.mcp.client
| 参数 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| enable | 是否启用MCP client | True |
| name | mcp client实例名称 | spring-ai-mcp-client |
| version | mcp client实例版本 | 1.0.0 |
| initialized | 是否创建时初始化 | true |
| request-timeout | 客户端请求超时时间 | 20s |
| type | 客户端类型(SYNC或ASYNC)。不支持混合 | SYNC |
| root-change-notification | 根上下文变更通知 | true |
| toolcallback.enabled | MCP工具回调与Spring AI的工具执行框架的集成 | true |
Client Starter Stdio
spring.ai.mcp.client.stdio
| 参数 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| servers-configuration | JSON格式的MCP服务器配置 | - |
| connections | stdio 连接配置 | |
| connections.[name].command | 命令 | |
| connections.[name].args | 参数 | |
| connections.[name].env | 环境变量 |
connections在yaml中直接配置
spring:
ai:
mcp:
client:
stdio:
root-change-notification: true
connections:
server1:
command: /path/to/server
args:
- --port=8080
- --mode=production
env:
API_KEY: your-api-key
DEBUG: "true"servers-configuration 配置文件方式
spring:
ai:
mcp:
client:
stdio:
servers-configuration: classpath:mcp-servers.json{
"mcpServers": {
"filesystem": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem",
"/Users/username/Desktop",
"/Users/username/Downloads"
]
}
}
}Client Starter Sse
spring.ai.mcp.client.sse
| 参数 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| connections | SSE连接配置 | - |
| connections.[name].url | - | |
| connections.[name].sse-endpoint | /sse |
spring:
ai:
mcp:
client:
sse:
connections:
server1:
url: http://localhost:8080
server2:
url: http://otherserver:8081
sse-endpoint: /custom-sseClient Starter Streamable-HTTP
spring.ai.mcp.client.streamable-http
| 参数 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| connections | SSE连接配置 | - |
| connections.[name].url | - | |
| connections.[name].sse-endpoint | /mcp |
Client Annoations
spring.ai.mcp.client.annotation-scanner.enabled default true
- @McpLogging - MCP server 返回的日志
- @McpSampling - 处理MCP server 对 大模型的请求
- @McpElicitation - 调用MCP前, 追问/向用户补充信息
- @McpProgress - MCP处理进度
- @McpToolListChanged - Handles notifications when the server’s tool list changes
- @McpResourceListChanged - Handles notifications when the server’s resource list changes
- @McpPromptListChanged - Handles notifications when the server’s prompt list changes
@Component
public class McpClientHandlers {
// 来自mcp服务端生成的日志
@McpLogging(clients = "server1")
public void handleLoggingMessage(LoggingMessageNotification notification) {
System.out.println("Received log: " + notification.level() +
" - " + notification.data());
}
// 来自 mcp服务端的调用大模型请求
@McpSampling(clients = "server1")
public CreateMessageResult handleSamplingRequest(CreateMessageRequest request) {
// Process the request and generate a response
String response = generateLLMResponse(request);
return CreateMessageResult.builder()
.role(Role.ASSISTANT)
.content(new TextContent(response))
.model("gpt-4")
.build();
}
// 来自mcp服务端的处理进度
@McpProgress(clients = "server1")
public void handleProgressNotification(ProgressNotification notification) {
double percentage = notification.progress() * 100;
System.out.println(String.format("Progress: %.2f%% - %s",
percentage, notification.message()));
}
@McpToolListChanged(clients = "server1")
public void handleToolListChanged(List<McpSchema.Tool> updatedTools) {
System.out.println("Tool list updated: " + updatedTools.size() + " tools available");
// Update local tool registry
toolRegistry.updateTools(updatedTools);
}
}@McpElicitation(clients = "interactive-server")
public ElicitResult handleInteractiveElicitation(ElicitRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> schema = request.requestedSchema();
Map<String, Object> userData = new HashMap<>();
// Check what information is being requested
if (schema != null && schema.containsKey("properties")) {
Map<String, Object> properties = (Map<String, Object>) schema.get("properties");
// Gather user input based on schema
if (properties.containsKey("name")) {
userData.put("name", promptUser("Enter your name:"));
}
if (properties.containsKey("email")) {
userData.put("email", promptUser("Enter your email:"));
}
if (properties.containsKey("preferences")) {
userData.put("preferences", gatherPreferences());
}
}
return new ElicitResult(ElicitResult.Action.ACCEPT, userData);
}
@McpElicitation(clients = "interactive-server")
public Mono<ElicitResult> handleAsyncElicitation(ElicitRequest request) {
return Mono.fromCallable(() -> {
// Async user interaction
Map<String, Object> userData = asyncGatherUserInput(request);
return new ElicitResult(ElicitResult.Action.ACCEPT, userData);
}).timeout(Duration.ofSeconds(30))
.onErrorReturn(new ElicitResult(ElicitResult.Action.CANCEL, null));
}
ClientCustomizer
@Component
public class CustomMcpSyncClientCustomizer implements McpSyncClientCustomizer {
@Override
public void customize(String serverConfigurationName, McpClient.SyncSpec spec) {
// Customize the request timeout configuration
spec.requestTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(30));
// Sets the root URIs that this client can access.
spec.roots(roots);
// Sets a custom sampling handler for processing message creation requests.
spec.sampling((CreateMessageRequest messageRequest) -> {
// Handle sampling
CreateMessageResult result = ...
return result;
});
// Sets a custom elicitation handler for processing elicitation requests.
spec.elicitation((ElicitRequest request) -> {
// handle elicitation
return new ElicitResult(ElicitResult.Action.ACCEPT, Map.of("message", request.message()));
});
// Adds a consumer to be notified when progress notifications are received.
spec.progressConsumer((ProgressNotification progress) -> {
// Handle progress notifications
});
// Adds a consumer to be notified when the available tools change, such as tools
// being added or removed.
spec.toolsChangeConsumer((List<McpSchema.Tool> tools) -> {
// Handle tools change
});
// Adds a consumer to be notified when the available resources change, such as resources
// being added or removed.
spec.resourcesChangeConsumer((List<McpSchema.Resource> resources) -> {
// Handle resources change
});
// Adds a consumer to be notified when the available prompts change, such as prompts
// being added or removed.
spec.promptsChangeConsumer((List<McpSchema.Prompt> prompts) -> {
// Handle prompts change
});
// Adds a consumer to be notified when logging messages are received from the server.
spec.loggingConsumer((McpSchema.LoggingMessageNotification log) -> {
// Handle log messages
});
}
}
// ASYNC
@Component
public class CustomMcpAsyncClientCustomizer implements McpAsyncClientCustomizer {
@Override
public void customize(String serverConfigurationName, McpClient.AsyncSpec spec) {
// Customize the async client configuration
spec.requestTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(30));
}
}Client Tool Filtering
@Component
public class CustomMcpToolFilter implements McpToolFilter {
@Override
public boolean test(McpConnectionInfo connectionInfo, McpSchema.Tool tool) {
// Filter logic based on connection information and tool properties
// Return true to include the tool, false to exclude it
// Example: Exclude tools from a specific client
if (connectionInfo.clientInfo().name().equals("restricted-client")) {
return false;
}
// Example: Only include tools with specific names
if (tool.name().startsWith("allowed_")) {
return true;
}
// Example: Filter based on tool description or other properties
if (tool.description() != null &&
tool.description().contains("experimental")) {
return false;
}
return true; // Include all other tools by default
}
}Client MCP Meta Converter
ChatModel chatModel = ...
String response = ChatClient.create(chatModel)
.prompt("Tell me more about the customer with ID 42")
.toolContext(Map.of("progressToken", "my-progress-token"))
.call()
.content();如果没有提供自定义转换器bean,启动器使用ToolContextToMcpMetaConverter.defaultConverter()
过滤MCP交换密钥(McpToolUtils)。TOOL_CONTEXT_MCP_EXCHANGE_KEY)
过滤掉带有空值的条目
作为元数据传递所有其他上下文条目
@Component
public class CustomToolContextToMcpMetaConverter implements ToolContextToMcpMetaConverter {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> convert(ToolContext toolContext) {
if (toolContext == null || toolContext.getContext() == null) {
return Map.of();
}
// Custom logic to convert tool context to MCP metadata
Map<String, Object> metadata = new HashMap<>();
// Example: Add custom prefix to all keys
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : toolContext.getContext().entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue() != null) {
metadata.put("app_" + entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
// Example: Add additional metadata
metadata.put("timestamp", System.currentTimeMillis());
metadata.put("source", "spring-ai");
return metadata;
}
}自动注入
@Autowired
private List<McpSyncClient> mcpSyncClients; // For sync client
// OR
@Autowired
private List<McpAsyncClient> mcpAsyncClients; // For async client当工具回调被启用时(spring.ai.mcp.client.toolcallback.enable),所有MCP客户端的注册MCP工具将作为ToolCallbackProvider实例提供
@Autowired
private SyncMcpToolCallbackProvider toolCallbackProvider;
ToolCallback[] toolCallbacks = toolCallbackProvider.getToolCallbacks();Server Starters
spring-ai-starter-mcp-server- Core server with STDIO transport supportspring-ai-starter-mcp-server-webmvc- Spring MVC-based SSE transport implementationspring-ai-starter-mcp-server-webflux- WebFlux-based SSE transport implementationspring-ai-starter-mcp-server-webmvc+spring.ai.mcp.server.protocol =STREAMABLEStreamable-HTTPspring-ai-starter-mcp-server-webflux+spring.ai.mcp.server.protocol =STREAMABLEStreamable-HTTPspring-ai-starter-mcp-server-webmvc+spring.ai.mcp.server.protocol =STATELESSStateless Streamable-HTTPspring-ai-starter-mcp-server-webflux+spring.ai.mcp.server.protocol =STATELESSStateless Streamable-HTTP
STDIO:本地进程通信的简单方案
描述:STDIO 协议是 Spring AI MCP Server 最基础的传输实现,它基于标准输入/输出流进行通信,无需网络协议支持。在技术实现上,客户端直接启动并管理服务器进程,通过向服务器标准输入(stdin)写入消息,从标准输出(stdout)读取消息完成交互
优势:
- 简单和安全性:数据传输完全在进程内存中进行,避免了网络传输的安全风险
- 无需网络配置:开发者只需通过命令行启动服务进程即可开始通信
- 低延迟低场景:适合需要快速响应的本地工具调用
劣势:
- 仅支持本地通信:无法跨网络或分布式环境使用
- 并发处理限制:采用同步机制,单线程处理请求,难以应对高并发场景
- 资源管理问题:每次请求都需要重建连接,无法有效复用资源
SSE:传统 HTTP 流式传输的单向方案
描述:SSE 协议是 Spring AI 早期版本中主流的远程传输方案,基于 HTML5 标准的服务器发送事件技术。在 Spring AI 框架中,SSE 分为两种实现方式:WebMVC 模式(基于 Servlet API)和 WebFlux 模式(基于响应式编程)
特点:服务器向客户端单向推送数据,允许服务器在建立连接后随时发送实时更新,无需客户端反复发起请求
优势:
- 实时推送能力:支持长连接保持,适合需要持续更新的场景
- 实现复杂度低:客户端只需通过浏览器原生支持的 EventSource 对象即可实现连接
- 传统环境集成方便:适合与现有 Spring MVC 项目无缝衔接
劣势:
- 高并发资源消耗:每个连接需占用约 80KB 内存,万级并发时可能导致服务器资源耗尽
- 连接稳定性差:在弱网环境下中断率高达 15%-30%,且不支持断线自动恢复
- 架构扩展性限制:强制要求服务器维护粘性会话,在负载均衡场景下增加了配置复杂度
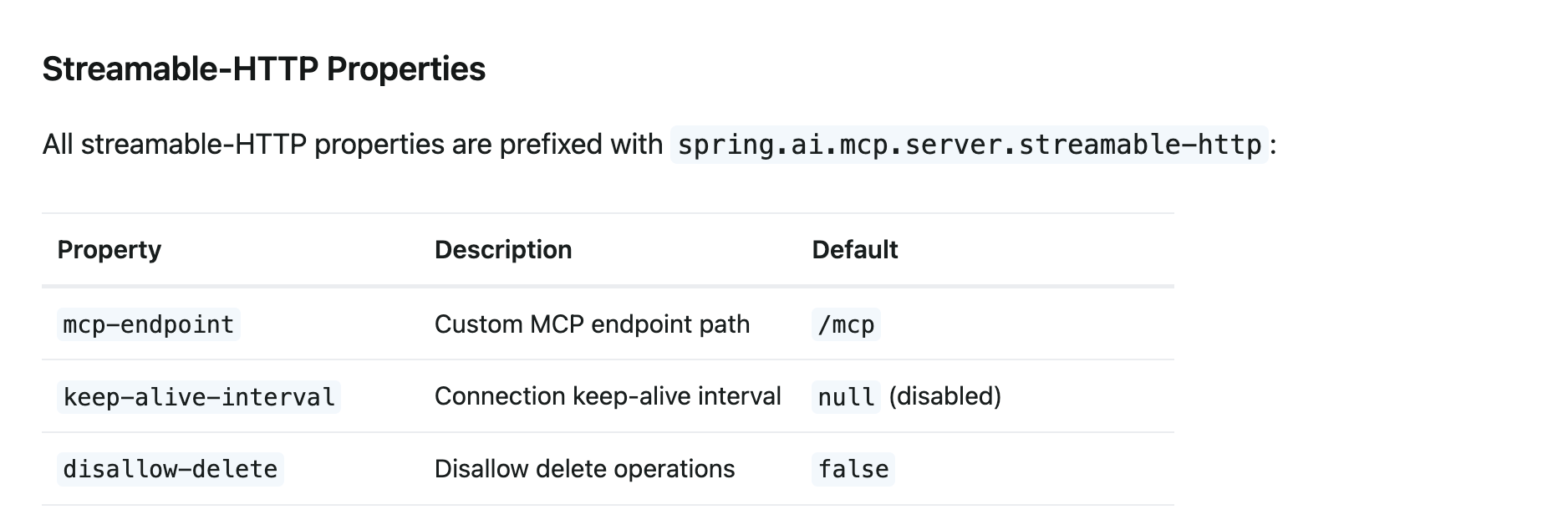
Streamable HTTP:平衡性能与状态的创新方案
描述 Streamable HTTP 协议是 MCP 协议在 2025 年 3 月的重大升级,它取代了原有的 HTTP+SSE 作为默认传输方式。Streamable HTTP 的核心创新在于统一了请求/响应端点,支持按需流式传输和会话管理,同时保留了 HTTP 协议的简洁性
特点:在高并发场景下,TCP 连接数仅为几十条,远低于 SSE 的上千条,显著降低了服务器资源压力。响应时间方面,Streamable HTTP 在 1000 并发用户测试中平均响应时间为 7.5ms,而 SSE 飙升至 1511ms,性能提升近 200 倍
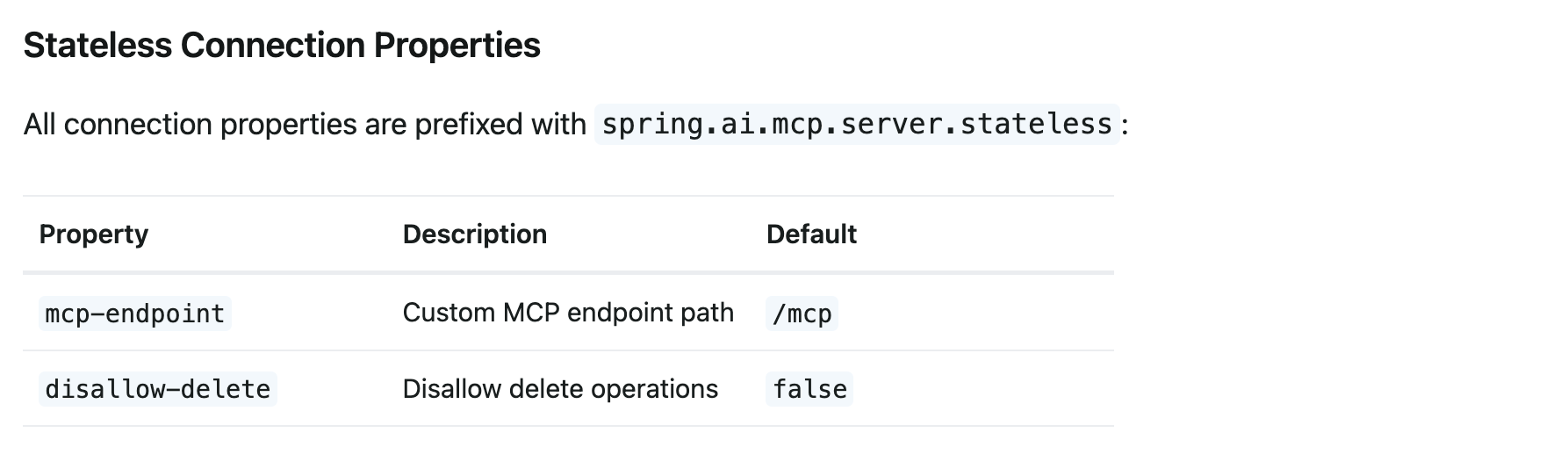
Stateless Streamable HTTP:无状态设计的极致优化
描述:Stateless Streamable HTTP 是 Streamable HTTP 的无状态变体,它通过移除会话状态管理,进一步优化了资源利用率和扩展性。Stateless 模式的核心理念是将状态管理责任从服务器转移到客户端,每次请求都包含完整的上下文信息
资源效率优势
- 内存消耗降至 5KB/请求以下,且在空闲状态下资源占用趋近于零
- 水平扩展能力强:请求可在服务器集群中任意路由,无需复杂的粘性会话机制
- 网络兼容性好:完全遵循标准 HTTP 语义,能更好地穿透企业防火墙
实现复杂度
- 客户端实现复杂:会话状态完全由客户端管理,增加了客户端实现复杂度
- 复杂交互处理困难:对于需要持续会话的复杂交互,可能导致客户端代码臃肿
- 断线重连要求高:客户端需主动传递所有必要信息,增加了实现难度
配置参数
spring.ai.mcp.server
| 参数 | 描述 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| enabled | 是否启用 | true |
| stdio | 是否启用stdio | False |
| name | server名称 | mcp-server |
| version | 版本 | 1.0.0 |
| instructions | 可选说明 | null |
| type | Server type (SYNC/ASYNC) | SYNC |
| capabilities.resource | 能否让模型访问/理解外部资源 | true |
| capabilities.tool | 能否调用注册的工具 / 函数 | true |
| capabilities.prompt | 能否使用结构化 Prompt / PromptTemplate | true |
| capabilities.completion | 能否进行“纯补全文本”模式 | true |
| resource-change-notification | Stateless 不适用 | true |
| prompt-change-notification | Stateless 不适用 | true |
| tool-change-notification | Stateless 不适用 | true |
| tool-response-mime-type | 响应mime , example image/png | - |
| annotation-scanner.enabled | True | |

Server Starter Tools
非注解
@Bean
public ToolCallbackProvider myTools(...) {
List<ToolCallback> tools = ...
return ToolCallbackProvider.from(tools);
}
// or using the low-level API:
@Bean
public List<McpServerFeatures.SyncToolSpecification> myTools(...) {
List<McpServerFeatures.SyncToolSpecification> tools = ...
return tools;
}注解
@Component
public class CalculatorTools {
@McpTool(name = "add", description = "Add two numbers together")
public int add(
@McpToolParam(description = "First number", required = true) int a,
@McpToolParam(description = "Second number", required = true) int b) {
return a + b;
}
}
@McpTool(name = "calculate-area",
description = "Calculate the area of a rectangle",
annotations = McpTool.McpAnnotations(
title = "Rectangle Area Calculator",
readOnlyHint = true,
destructiveHint = false,
idempotentHint = true
))
public AreaResult calculateRectangleArea(
@McpToolParam(description = "Width", required = true) double width,
@McpToolParam(description = "Height", required = true) double height) {
return new AreaResult(width * height, "square units");
}
// context 参数注入
@McpTool(name = "process-data", description = "Process data with request context")
public String processData(
McpSyncRequestContext context,
@McpToolParam(description = "Data to process", required = true) String data) {
// 返回给客户端的info日志
// Send logging notification
context.info("Processing data: " + data);
// Send progress notification (using convenient method)
context.progress(p -> p.progress(0.5).total(1.0).message("Processing..."));
// Ping the client
context.ping();
return "Processed: " + data.toUpperCase();
}
// 动态参数
@McpTool(name = "flexible-tool", description = "Process dynamic schema")
public CallToolResult processDynamic(CallToolRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> args = request.arguments();
// Process based on runtime schema
String result = "Processed " + args.size() + " arguments dynamically";
return CallToolResult.builder()
.addTextContent(result)
.build();
}
// 有进度反馈
@McpTool(name = "long-task", description = "Long-running task with progress")
public String performLongTask(
McpSyncRequestContext context,
@McpToolParam(description = "Task name", required = true) String taskName) {
// Access progress token from context
String progressToken = context.request().progressToken();
if (progressToken != null) {
// 处理进度
context.progress(p -> p.progress(0.0).total(1.0).message("Starting task"));
// Perform work...
context.progress(p -> p.progress(1.0).total(1.0).message("Task completed"));
}
return "Task " + taskName + " completed";
}
Server Starter Resource
非注解
@Bean
public List<McpServerFeatures.SyncResourceSpecification> myResources(...) {
var systemInfoResource = new McpSchema.Resource(...);
var resourceSpecification = new McpServerFeatures.SyncResourceSpecification(systemInfoResource, (exchange, request) -> {
try {
var systemInfo = Map.of(...);
String jsonContent = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(systemInfo);
return new McpSchema.ReadResourceResult(
List.of(new McpSchema.TextResourceContents(request.uri(), "application/json", jsonContent)));
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to generate system info", e);
}
});
return List.of(resourceSpecification);
}注解
@Component
public class ResourceProvider {
@McpResource(
uri = "config://{key}",
name = "Configuration",
description = "Provides configuration data")
public String getConfig(String key) {
return configData.get(key);
}
}
// 返回对象是ReadResourceResult
@McpResource(
uri = "user-profile://{username}",
name = "User Profile",
description = "Provides user profile information")
public ReadResourceResult getUserProfile(String username) {
String profileData = loadUserProfile(username);
return new ReadResourceResult(List.of(
new TextResourceContents(
"user-profile://" + username,
"application/json",
profileData)
));
}
// context参数注入
@McpResource(
uri = "data://{id}",
name = "Data Resource",
description = "Resource with request context")
public ReadResourceResult getData(
McpSyncRequestContext context,
String id) {
// Send logging notification using convenient method
context.info("Accessing resource: " + id);
// Ping the client
context.ping();
String data = fetchData(id);
return new ReadResourceResult(List.of(
new TextResourceContents("data://" + id, "text/plain", data)
));
}Server Starter Prompts
非注解
@Bean
public List<McpServerFeatures.SyncPromptSpecification> myPrompts() {
var prompt = new McpSchema.Prompt("greeting", "A friendly greeting prompt",
List.of(new McpSchema.PromptArgument("name", "The name to greet", true)));
var promptSpecification = new McpServerFeatures.SyncPromptSpecification(prompt, (exchange, getPromptRequest) -> {
String nameArgument = (String) getPromptRequest.arguments().get("name");
if (nameArgument == null) { nameArgument = "friend"; }
var userMessage = new PromptMessage(Role.USER, new TextContent("Hello " + nameArgument + "! How can I assist you today?"));
return new GetPromptResult("A personalized greeting message", List.of(userMessage));
});
return List.of(promptSpecification);
}注解
@Component
public class PromptProvider {
@McpPrompt(
name = "greeting",
description = "Generate a greeting message")
public GetPromptResult greeting(
@McpArg(name = "name", description = "User's name", required = true)
String name) {
String message = "Hello, " + name + "! How can I help you today?";
return new GetPromptResult(
"Greeting",
List.of(new PromptMessage(Role.ASSISTANT, new TextContent(message)))
);
}
}
@McpPrompt(
name = "personalized-message",
description = "Generate a personalized message")
public GetPromptResult personalizedMessage(
@McpArg(name = "name", required = true) String name,
@McpArg(name = "age", required = false) Integer age,
@McpArg(name = "interests", required = false) String interests) {
StringBuilder message = new StringBuilder();
message.append("Hello, ").append(name).append("!\n\n");
if (age != null) {
message.append("At ").append(age).append(" years old, ");
// Add age-specific content
}
if (interests != null && !interests.isEmpty()) {
message.append("Your interest in ").append(interests);
// Add interest-specific content
}
return new GetPromptResult(
"Personalized Message",
List.of(new PromptMessage(Role.ASSISTANT, new TextContent(message.toString())))
);
}Server Starter Completion
非注解
@Bean
public List<McpServerFeatures.SyncCompletionSpecification> myCompletions() {
var completion = new McpServerFeatures.SyncCompletionSpecification(
new McpSchema.PromptReference(
"ref/prompt", "code-completion", "Provides code completion suggestions"),
(exchange, request) -> {
// Implementation that returns completion suggestions
return new McpSchema.CompleteResult(List.of("python", "pytorch", "pyside"), 10, true);
}
);
return List.of(completion);
}注解
@Component
public class CompletionProvider {
@McpComplete(prompt = "city-search")
public List<String> completeCityName(String prefix) {
return cities.stream()
.filter(city -> city.toLowerCase().startsWith(prefix.toLowerCase()))
.limit(10)
.toList();
}
}
//CompleteRequest.CompleteArgument
@McpComplete(prompt = "travel-planner")
public List<String> completeTravelDestination(CompleteRequest.CompleteArgument argument) {
String prefix = argument.value().toLowerCase();
String argumentName = argument.name();
// Different completions based on argument name
if ("city".equals(argumentName)) {
return completeCities(prefix);
} else if ("country".equals(argumentName)) {
return completeCountries(prefix);
}
return List.of();
}
//CompleteResult
@McpComplete(prompt = "code-completion")
public CompleteResult completeCode(String prefix) {
List<String> completions = generateCodeCompletions(prefix);
return new CompleteResult(
new CompleteResult.CompleteCompletion(
completions,
completions.size(), // total
hasMoreCompletions // hasMore flag
)
);
}Demo
stdio
# Using spring-ai-starter-mcp-server
spring:
ai:
mcp:
server:
name: stdio-mcp-server
version: 1.0.0
type: SYNCwebmvc
# Using spring-ai-starter-mcp-server-webmvc
spring:
ai:
mcp:
server:
name: webmvc-mcp-server
version: 1.0.0
type: SYNC
instructions: "This server provides weather information tools and resources"
sse-message-endpoint: /mcp/messages
capabilities:
tool: true
resource: true
prompt: true
completion: truewebflux
# Using spring-ai-starter-mcp-server-webflux
spring:
ai:
mcp:
server:
name: webflux-mcp-server
version: 1.0.0
type: ASYNC # Recommended for reactive applications
instructions: "This reactive server provides weather information tools and resources"
sse-message-endpoint: /mcp/messages
capabilities:
tool: true
resource: true
prompt: true
completion: trueserver
@Service
public class WeatherService {
@Tool(description = "Get weather information by city name")
public String getWeather(String cityName) {
// Implementation
}
}
@SpringBootApplication
public class McpServerApplication {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(McpServerApplication.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(McpServerApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ToolCallbackProvider weatherTools(WeatherService weatherService) {
return MethodToolCallbackProvider.builder().toolObjects(weatherService).build();
}
}